NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Neomycin is a broad spectrum aminoglycoside antibiotic whose current use is limited to oral and topical administration. Neomycin has minimal oral absorption and its use has not been linked to instances of acute liver injury.
Background
Neomycin (nee" oh mye' sin) is an aminoglycoside with a broad spectrum of activity against both gram positive and gram negative organisms. Like other aminoglycosides, neomycin is thought to act by binding to bacterial ribosomes and inhibiting protein synthesis. Neomycin has activity against many aerobic gram negative and gram positive bacteria, including the major E. coli species resident in the colon as well as the enteropathogenic forms of E. coli known to cause traveler’s diarrhea. Like other aminoglycosides, neomycin is poorly absorbed orally. The lack of absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is the basis of the main use of neomycin, as an oral agent to suppress intestinal bacterial flora. Oral neomycin is indicated for treatment of infectious diarrhea, for suppression of intestinal bacterial flora in patients undergoing colorectal surgery, and as a means of decreasing colonic bacteria and production of ammonia in hepatic encephalopathy. Topical neomycin is used for burns, wounds and ulcerations and as otic suspensions for external otitis. Neomycin is available in multiple generic forms including oral tablets of 500 mg. The typical adult dose of neomycin is 1 to 3 grams daily in four divided doses. Long term therapy should be avoided because of the possibility of some systemic absorption and the high rate of oto- and nephrotoxicity associated with neomycin use. Other adverse events include nausea, diarrhea, and Clostridium difficile related colitis.
Hepatotoxicity
Oral and topical therapy with neomycin has not been linked serum alkaline phosphatase or aminotransferase elevations, and no convincing cases of symptomatic or icteric hepatotoxicity due to oral neomycin have been published. The poor absorption of neomycin makes it unlikely that systemic levels of the drug that might cause liver injury could be achieved. Furthermore, the ototoxicity of absorbed neomycin is likely to supervene before liver toxicity would occur.
References to the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of neomycin are provided in the Overview section on the Aminoglycosides.
Drug Class: Aminoglycosides
Other Drugs in the Class: Amikacin, Gentamicin, Plazomicin, Streptomycin, Tobramycin
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Neomycin – Generic
DRUG CLASS
Aminoglycosides
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
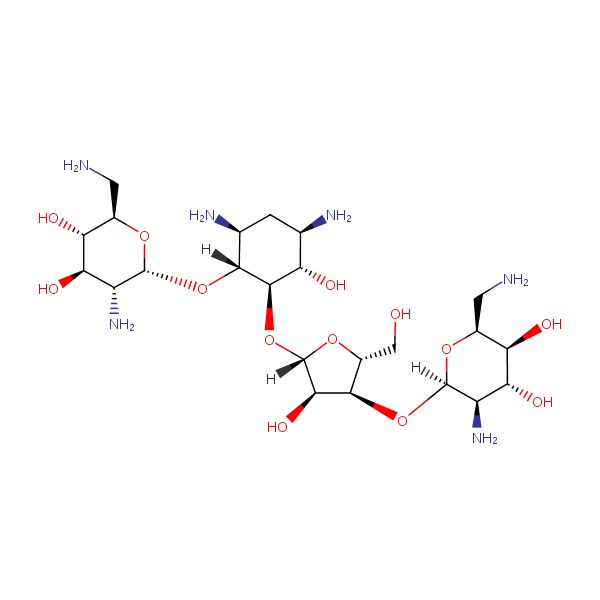
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NO. | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neomycin | 1404-04-2 | Unspecified |
 |
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- Adaptive Cross-Resistance to Aminoglycoside Antibiotics in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Induced by Topical Dosage of Neomycin.[Chemotherapy. 2017]Adaptive Cross-Resistance to Aminoglycoside Antibiotics in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Induced by Topical Dosage of Neomycin.Uemura S, Yokota SI, Shiraishi T, Kitagawa M, Hirayama S, Kyan R, Mizuno H, Sawamoto K, Inoue H, Miyamoto A, et al. Chemotherapy. 2017; 62(2):121-127. Epub 2016 Oct 29.
- Systemic contact dermatitis following oral neomycin therapy.[Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2020]Systemic contact dermatitis following oral neomycin therapy.Carnicle JM, Tran TV, McKissack SS. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2020 Aug 24; 34(1):89-90. Epub 2020 Aug 24.
- Topical aminoglycoside ototoxicity: attempting to protect the cochlea.[Acta Otolaryngol. 2000]Topical aminoglycoside ototoxicity: attempting to protect the cochlea.Conlon BJ, Smith DW. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000 Aug; 120(5):596-9.
- Review Targeted modifications of neomycin and paromomycin: Towards resistance-free antibiotics?[Bioorg Chem. 2022]Review Targeted modifications of neomycin and paromomycin: Towards resistance-free antibiotics?Obszynski J, Loidon H, Blanc A, Weibel JM, Pale P. Bioorg Chem. 2022 Sep; 126:105824. Epub 2022 May 12.
- Review Plazomicin.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Plazomicin.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Neomycin - LiverToxNeomycin - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...