NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Flavoxate is a synthetic anticholinergic agent that is used for treatment of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder syndrome. Flavoxate has not been implicated in causing liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent acute liver injury.
Background
Flavoxate (flay vox' ate) is a synthetic quaternary ammonium anticholinergic which inhibits the muscarinic actions of acetylcholine on autonomic nerve endings, decreasing the smooth muscle tone of bladder and gastrointestinal tract. Flavoxate has broad activity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, but its highly polar quaternary ammonium group makes it less likely to cross lipid membranes such as the blood brain barrier, which is believed to decrease the potential for central nervous system effects. Flavoxate increases bladder capacity and decreases urinary frequency and urgency. Flavoxate was approved for use in the United States in 1970 and continues to be used to treat the symptoms of cystitis and overactive bladder syndrome. Flavoxate is available in tablets of 100 mg in several generic forms and previously under the brand name Urispas. The typically recommended oral dose in adults is 100 to 200 mg three or four times daily. Common side effects are those of parasympathetic stimulation and include dryness of the mouth and eyes, decreased sweating, headache, visual blurring, constipation, urinary retention, impotence, tachycardia and palpitations, anxiety, restlessness and in some instances agitation and delusions. Anticholinergic agents can precipitate acute narrow angle glaucoma and acute urinary retention.
Hepatotoxicity
Like other anticholinergic agents, flavoxate has not been linked to episodes of liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver injury. A major reason for its safety may relate to the low daily dose.
References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of anticholinergics are given together after the Overview section on Anticholinergic Agents.
Drug Class: Anticholinergic Agents
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Flavoxate – Generic, Urispas®
DRUG CLASS
Anticholinergic Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
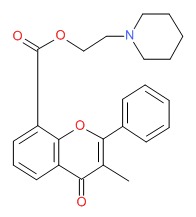
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flavoxate | 15301-69-6 | C24-H25-N-O4 |
 |
- Review Anticholinergic drugs versus other medications for overactive bladder syndrome in adults.[Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007]Review Anticholinergic drugs versus other medications for overactive bladder syndrome in adults.Roxburgh C, Cook J, Dublin N. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17; 2007(4):CD003190. Epub 2007 Oct 17.
- Review Anticholinergic drugs versus other medications for overactive bladder syndrome in adults.[Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007]Review Anticholinergic drugs versus other medications for overactive bladder syndrome in adults.Roxburgh C, Cook J, Dublin N. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18; (3):CD003190. Epub 2007 Jul 18.
- Review Oxybutynin.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Oxybutynin.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Fesoterodine.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Fesoterodine.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Darifenacin.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Darifenacin.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Flavoxate - LiverToxFlavoxate - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...