NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Dutasteride is a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor used in the therapy of symptomatic benign prostatic hypertrophy. Dutasteride is associated with a low rate of transient serum aminotransferase elevations, but has yet to be linked to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury.
Background
Dutasteride (doo tas' ter ide) was the second 5-alpha reductase inhibitor to be approved in the United States for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hypertrophy. Dutasteride inhibits the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone, which is important in the development and maintenance of prostatic hyperplasia. Dihydrotesterone levels decrease during dutasteride therapy, but serum testosterone levels do not. Dutasteride usually takes several months to have an effect on prostate size and the symptoms of prostatic hypertrophy (urinary hesitancy and poor stream), unlike the alpha-1 adrenergic receptor blockers (alpha blockers) which have a more immediate effect. Dutasteride was approved for use in the United States in 2001 and is available in 0.5 mg capsules generically and under the trade name Avodart. A fixed dose combination of dutasteride (0.5 mg) with tamsulosin (0.4 mg: an alpha blocker) is available under the trade name Jalyn. The recommended dose of dutasteride is 0.5 mg once daily. Dutasteride is usually given long term and an effect is usually not seen until 3 to 6 months of therapy. Side effects are uncommon, but include impotence and decreased libido, ejaculation disorders, gynecomastia, dizziness and fatigue. Dutasteride also decreases serum PSA levels which should be monitored during therapy.
Hepatotoxicity
Dutasteride has been associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations that, in controlled trials, was no higher than with placebo therapy. These elevations were transient and rarely required dose modification. There have been no published reports of clinically apparent liver injury due to dutasteride therapy.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Mechanism of Injury
The cause of the minor serum aminotransferase elevations associated with dutasteride is not known. Dutasteride is an azosteroid and is extensively metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 system (predominantly CYP 3A4 and 3A5).
References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of dutasteride are given in the Overview section on the 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors.
Drug Class: Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Agents, 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Dutasteride – Avodart®
DRUG CLASS
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
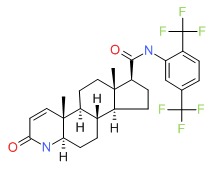
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dutasteride | 164656-23-9 | C27-H30-F6-N2-O2 |
 |
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- Review Finasteride.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Finasteride.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Alpha Reductase Inhibitors.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Alpha Reductase Inhibitors.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Improvements in benign prostatic hyperplasia-specific quality of life with dutasteride, the novel dual 5alpha-reductase inhibitor.[BJU Int. 2003]Improvements in benign prostatic hyperplasia-specific quality of life with dutasteride, the novel dual 5alpha-reductase inhibitor.O'Leary MP, Roehrborn C, Andriole G, Nickel C, Boyle P, Höfner K. BJU Int. 2003 Aug; 92(3):262-6.
- Review Dutasteride: a novel dual inhibitor of 5alpha-reductase for benign prostatic hyperplasia.[Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005]Review Dutasteride: a novel dual inhibitor of 5alpha-reductase for benign prostatic hyperplasia.Djavan B, Milani S, Fong YK. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005 Feb; 6(2):311-7.
- Review Doxazosin.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Doxazosin.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Dutasteride - LiverToxDutasteride - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...