NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Doxepin is a tricyclic antidepressant that widely used in the therapy of depression. Doxepin can cause mild and transient serum enzyme elevations but is a rare cause of clinically apparent acute cholestatic liver injury.
Background
Doxepin (dox' e pin) is a dibenzoxepine derived tricyclic antidepressant which acts by inhibition of serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake within synaptic clefts in the central nervous system, thus increasing brain levels of these neurotransmitters. Doxepin is indicated for therapy of depression or anxiety and was approved for this indication in the United States in 1969 and it is still widely used, with more than 2 million prescriptions being filled yearly. Doxepin is available in generic forms and under the brand names of Sinequan in capsules of 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 and 150 mg as well as an oral solution. The recommended adult dose for depression is 25 to 75 mg daily in divided doses, increasing gradually to a maximum of 300 mg daily. Doxepin can also be given as a single nighttime dose (maximum dose of 150 mg). Common side effects include dizziness, headache, drowsiness, restlessness, confusion, gastrointestinal upset, nausea, increased appetite, weight gain, blurred vision, dry mouth, urinary retention, rash and hypersensitivity reactions. Rare but potentially severe adverse events include suicidal thoughts and behaviors and acute glaucoma.
Hepatotoxicity
Liver test abnormalities have been reported to occur in up to 16% of patients being treated with tricyclic antidepressants, but elevations are uncommonly above 3 times the upper limit of normal. The aminotransferase abnormalities are usually mild, asymptomatic and transient, reversing even with continuation of medication. Rare instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury have been reported due to doxepin, but the number of cases have been too few to characterize the clinical features. Recurrent jaundice and marked aminotransferase elevations with repeated exposures to doxepin has been reported. Most cases have been mild and deaths from acute liver failure or chronic injury have not been reported.
Likelihood score: C (possible rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Mechanism of Injury
The mechanism by which doxepin causes serum aminotransferase elevation is not known. It undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism and a possible cause of liver injury is production of a toxic intermediate of metabolism.
Outcome and Management
The serum aminotransferase elevations that occur on doxepin therapy are usually self-limited and do not require dose modification or discontinuation of therapy. The acute liver injury associated with doxepin has been self-limited and no cases of acute liver failure or chronic liver disease due to doxepin have been reported. Rechallenge with doxepin is likely to cause a prompt recurrence of the liver injury and should be avoided. Patients with clinically apparent doxepin induced liver injury may have cross sensitivity to injury from other tricyclic antidepressants and phenothiazines, but generally tolerate other forms of antidepressant medications such as the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Drug Class: Antidepressant Agents
Other Drugs in the Subclass, Tricyclics: Amitriptyline, Amoxapine, Clomipramine, Desipramine, Imipramine, Nortriptyline, Protriptyline, Trimipramine
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Doxepin – Sinequan®
DRUG CLASS
Antidepressant Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
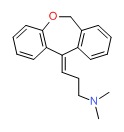
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Doxepin | 1668-19-5 | C19-H21-N-O |
 |
ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
References updated: 08 January 2018
- Zimmerman HJ. Tricyclic antidepressants. In, Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1999, pp. 495-8.(Expert review of hepatotoxicity published in 1999 mentions that hepatic injury caused by tricyclic antidepressants is less frequent and less consistent than with monamine oxidase inhibitors).
- Larrey D, Ripault MP. Hepatotoxicity of psychotropic drugs and drugs of abuse. In, Kaplowitz N, DeLeve LD, eds. Drug-induced liver disease. 3rd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013, pp. 443-62.(Review of tricylic antidepressant hepatotoxicity mentions that doxepin has been implicated in rare instances of short latency onset, cholestatic hepatitis).
- O'Donnell JM, Shelton RC. Pharmacotherapy of depression and anxiety disorders. In, Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 121th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2011, pp. 397-416.(Textbook of pharmacology and therapeutics).
- Klerman GL, Cole JO. Clinical pharmacology of imipramine and related antidepressant compounds. Pharmacol Rev 1965; 17: 101-41. [PubMed: 14294030](Extensive review of structure, pharmacology, clinical effects, mechanisms of action, drug interactions, and side effects of tricyclic antidepressants; jaundice arises in 0.5 to 1% of treated patients and usually resolves rapidly with stopping).
- Clarke AE, Maritz VM, Denborough MA. Phenothiazines and jaundice. Aust N Z J Med 1972; 2: 376-82. [PubMed: 4144624](Chlorpromazine and amitriptyline cause precipitation of proteins when added to human bile in vitro and hepatotoxicity of these agents may relate to this characteristic).
- Fiori MG. Tricyclic antidepressants: a review of their toxicology. Curr Dev Psychopharmacol 1977; 4: 71-110. [PubMed: 340145](Review of cardiac, hepatic, neurological, fetal and psychotoxicity of tricyclic antidepressants; most cases of hepatotoxicity have been attributed to hypersensitivity, but tricyclics are taken up and extensively metabolized by hepatocytes).
- Døssing M, Andreasen PB. Drug-induced liver disease in Denmark. An analysis of 572 cases of hepatotoxicity reported to the Danish Board of Adverse Reactions to Drugs. Scand J Gastroenterol 1982; 17: 205-11. [PubMed: 6982502](Among 572 cases of drug induced liver disease seen between 1968-78 in Denmark, psychotropic agents accounted for 93 cases, 54 of which were due to chlorpromazine; tricyclics not specifically mentioned).
- Larrey D, Rueff B, Pessayre D, Algard M, Geneve J, Benhamou JP. Cross hepatotoxicity between tricyclic antidepressants. Gut 1986; 87-90. [PMC free article: PMC1433318] [PubMed: 3721296](39 year old woman developed abdominal pain 2 weeks after starting amineptine [a tricyclic antidepressant], with fever and eosinophilia [bilirubin 1.2 mg/dL, ALT 1360 U/L, Alk P 1.5 times ULN] resolving rapidly on stopping, but recurring 7 days after starting clomipramine [ALT 1050 U/L, Alk P 1.5 times ULN], again resolving rapidly upon stopping).
- Geneve J, Larrey D, Pessayre D, Benhamou JP. Structure tricyclique des medicaments et hepatotoxicite. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 1987; 11: 242-9. [PubMed: 2884161](Review of structural similarity and hepatotoxicity of tricyclic antidepressants focusing on amineptine, imipramine and amitriptyline).
- Pirmohamed MKL, Kittringham NR, Parkl BK. Idiosyncratic reactions to antidepressants: a review of the possible mechanism and predisposing factors. Pharm Ther 1992; 53: 105-25. [PubMed: 1641399](Review of idiosyncratic reactions to antidepressants; possible mechanism of injury being production of a chemically reactive metabolite that is either directly toxic or induces a hypersensitivity reaction).
- Keegan AD. Doxepin-induced recurrent acute hepatitis. Aust N Z J Med 1993; 23: 523. [PubMed: 8297287](50 year old man with 3 episodes of jaundice following use of doxepin for 1-2 days [bilirubin 3.3, 16.4 and 5.5 mg/dL, ALT >1500 U/L, Alk P]).
- Berson A, Fréneaux E, Larrey D, Lepage V, Douay C, Mallet C. Possible role of HLA in hepatotoxicity. An exploratory study. J Hepatol 1994; 20: 336-42. [PubMed: 8014443](Human leukocyte antigen [HLA] haplotypes done on 71 patients with drug induced liver disease; among 12 due to tricyclics [7 amineptine, 3 amitriptyline and 2 clomipramine], 6 [50%] were HLA A11 positive including 2 of the 3 amitriptyline cases; 12% in controls had this allele).
- Marttila M, Jaaskelainen J, Jarvi R, Romanov M, Miettinen E, Sorri P, Ahlfors U, et al. A double-blind study comparing the efficacy and tolerability of mirtazapine and doxepin in patients with major depression. Eur Neuropsychopharm 1995; 15: 441-6. [PubMed: 8998395](Controlled trial of doxepin vs mirtazapine in 163 patients with depression found no statistically significant changes in biochemical tests from baseline in either group and no instances of clinically apparent liver injury).
- Remy AL, Larrey D, Pageaux GP, Desprez D, Ramos J, Michel H. Cross hepatotoxicity between tricyclic antidepressants and phenothiazines. Eur J Gastroenterol 1995; 7: 373-6. [PubMed: 7600146](65 year old woman developed fatigue and serum enzyme elevations [ALT ~1300 U/L; Alk P ~380 U/L] 1 month after starting trimipramine; 3 years later she developed nausea and ALT elevations 10 days after starting desipramine [ALT ~250 U/L], and 2 years later developed abdominal pain and fever and enzyme elevations [ALT ~1100 U/L, Alk P ~510 U/L] 8 days after starting cyamemazine; each time with rapid recovery and no jaundice).
- Allison DB, Mentore JL, Heo M, Chandler LP, Cappelleri JC, Infante MC, Weiden PJ. Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: a comprehensive research synthesis. Am J Psychiatry 1999; 156: 1686-96. [PubMed: 10553730](Systematic review of 81 articles on weight change with antipsychotics; using change after 10 weeks to compare: clozapine +5.7, olanzapine +4.2, chlorpromazine +4.2, risperidone +1.7, loxapine +0.6, haloperidol +0.5, ziprasidone +0.3, molindone -0.1, and pimozide -2.7 kilograms).
- Grohmann R, Rüther E, Engel RR, Hippius H. Assessment of adverse drug reactions in psychiatric inpatients with the AMSP drug safety program: methods and first results for tricyclic antidepressants and SSRIs. Pharmacopsychiatry 1999; 32: 21-8. [PubMed: 10071179](Analysis of reporting of adverse events among inpatients in 29 German hospitals between 1993 to 1997; 896 severe adverse events among 48,564 patients [1.8%], both total and hepatic events were more common with tricyclics than SSRIs).
- Carvajal García-Pando A, García del Pozo J, Sánchez AS, Velasco MA, Rueda de Castro AM, Lucena MI. Hepatotoxicity associated with the new antidepressants. J Clin Psychiatry 2002; 63: 135-7. [PubMed: 11874214](Analysis of cases of hepatotoxicity from antidepressants in Spanish Pharmacovigilance System from 1989-1999, identified 99 cases; among SSRIs, 26 due to fluoxetine, 14 paroxetine, 6 fluvoxamine, 5 sertraline, 3 venlafaxine and 2 citalopram; among tricyclics, 16 clomipramine 7 amitriptyline, 6 imipramine; among miscellaneous, 3 nefazodone and 1 trazodone; but all similar in rate ~1-3 per 100,000 patient-years of exposure except for nefazodone=29/100,000; doxepin not mentioned.).
- Lucena M, Carvajal A, Andrade R, Velasco A. Antidepressant-induced hepatotoxicity. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2003; 2: 249-62. [PubMed: 12904104](Review of hepatotoxicity of antidepressants; antidepressant use has increased markedly between 1992 and 2002, accounting for 5% of cases of hepatotoxicity; SSRIs are less likely to cause injury than tricyclics and MAO inhibitors; range of presentations, typically self-limited and rapid recovery; doxepin is listed but not specifically discussed).
- Milkiewicz P, Chilton AP, Hubscher SG, Elias E. Antidepressant induced cholestasis: hepatocellular redistribution of multidrug resistant protein(MRP2). Gut 2003; 52: 300-3. [PMC free article: PMC1774956] [PubMed: 12524417](Two cases; 30 year old woman developed jaundice 8 weeks after starting citalopram [bilirubin 4.4 mg/dL, AST 33 U/L, Alk P 637 U/L], resolving within 2 months of stopping; 63 year old man developed jaundice 3 months after starting dothiepin [a tricyclic antidepressant related to doxepin that is not available in the US] with bilirubin 9.4 mg/dL, AST 40 U/L, Alk P 600 U/L], resolving within 3 months of stopping on corticosteroids and later tolerating fluoxetine for 12 months, but redeveloping jaundice 2 months after starting paroxetine [bilirubin 15.2 mg/dL, AST 36 U/L, Alk P 544 U/L], resolving within 6 months of stopping).
- Degner D, Grohmann R, Kropp S, Rüther E, Bender S, Engel RR, Schmidt LG. Severe adverse drug reactions of antidepressants: results of the German multicenter drug surveillance program AMSP. Pharmacopsychiatry 2004; 37 Suppl 1: S39-45. [PubMed: 15052513](53,042 patients treated with antidepressants in 35 psychiatric hospitals in Germany from 1993-2000 were monitored for adverse drug reactions; increased liver enzymes reported in 16% on tricyclics, 5.5% on SSRIs and 12% of monamine oxidase inhibitors).
- Sabaté M, Ibáñez L, Pérez E, Vidal X, Buti M, Xiol X, Mas A, et al. Risk of acute liver injury associated with the use of drugs: a multicentre population survey. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007; 25: 1401-9. [PubMed: 17539979](Among 126 cases of drug induced liver injury seen in Spain between 1993-2000, 3 were due to amitriptyline with a relative risk of 14.2: estimated frequency of 6 per 100,000 person-year exposures).
- DeSanty KP, Amabile CM. Antidepressant-induced liver injury. Ann Pharmacother 2007; 41: 1201-11. [PubMed: 17609231](Review of drug induced liver injury and summary analysis of reports of injury from MAO inhibitors, SSRIs, tricyclics and atypical agents).
- Chalasani N, Fontana RJ, Bonkovsky HL, Watkins PB, Davern T, Serrano J, Yang H, Rochon J; Drug Induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN). Causes, clinical features, and outcomes from a prospective study of drug-induced liver injury in the United States. Gastroenterology 2008; 135: 1924-34. [PMC free article: PMC3654244] [PubMed: 18955056](Among 300 cases of drug induced liver disease in the US collected from 2004 to 2008, one case was attributed to a tricyclic antidepressant [amitriptyline], doxepin not listed).
- Reuben A, Koch DG, Lee WM; Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Drug-induced acute liver failure: results of a U.S. multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology 2010; 52: 2065-76. [PMC free article: PMC3992250] [PubMed: 20949552](Among 1198 patients with acute liver failure enrolled in a US prospective study between 1998 and 2007, 133 were attributed to drug induced liver injury, but none were linked to a tricyclic antidepressant).
- Molleston JP, Fontana RJ, Lopez MJ, Kleiner DE, Gu J, Chalasani N; Drug-induced Liver Injury Network. Characteristics of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury in children: results from the DILIN prospective study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2011; 53: 182-9. [PMC free article: PMC3634369] [PubMed: 21788760](Among 30 children with suspected drug induced liver injury, half were due to antimicrobials and the rest largely due to CNS agents; one case was attributed to amitriptyline, but no other tricyclic antidepressant was listed).
- Björnsson ES, Bergmann OM, Björnsson HK, Kvaran RB, Olafsson S. Incidence, presentation and outcomes in patients with drug-induced liver injury in the general population of Iceland. Gastroenterology 2013; 144: 1419-25. [PubMed: 23419359](In a population based study of drug induced liver injury from Iceland, 96 cases were identified over a 2 year period, but none were attributed to tricyclic antidepressants, none of which were among the top 48 drugs dispensed in Iceland during the period).
- Park SH, Ishino R. Liver injury associated with antidepressants. Curr Drug Saf 2013; 8: 207-23. [PubMed: 23914755](Review of antidepressant induced liver injury; doxepin is not discussed).
- Hernández N, Bessone F, Sánchez A, di Pace M, Brahm J, Zapata R, A Chirino R, et al. Profile of idiosyncratic drug induced liver injury in Latin America. An analysis of published reports. Ann Hepatol 2014; 13: 231-9. [PubMed: 24552865](Systematic review of literature of drug induced liver injury in Latin American countries published from 1996 to 2012 identified 176 cases, one of which was attributed to amitriptyline but none to doxepin).
- Chalasani N, Bonkovsky HL, Fontana R, Lee W, Stolz A, Talwalkar J, Reddy KR, et al.; United States Drug Induced Liver Injury Network. Features and outcomes of 899 patients with drug-induced liver injury: The DILIN Prospective Study. Gastroenterology 2015; 148: 1340-52.e7. [PMC free article: PMC4446235] [PubMed: 25754159](Among 899 cases of drug induced liver injury enrolled in a US prospective study between 2004 and 2013, 20 cases [2%] were attributed to antidepressants, but only one to a tricyclic [imipramine] and none to doxepin).
- Friedrich ME, Akimova E, Huf W, Konstantinidis A, Papageorgiou K, Winkler D, Toto S, et al. Drug-induced liver injury during antidepressant treatment: results of AMSP, a drug surveillance program. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2016; 19. pii: pyv126. [PMC free article: PMC4851269] [PubMed: 26721950](Monitoring of 184,234 inpatients in 80 psychiatric hospitals for liver injury during antidepressant treatment identified 149 cases including 7 of 12,412 who were receiving doxepine, a rate [0.06%] similar to other antidepressants [overall 0.08%]).
- Ferrajolo C, Scavone C, Donati M, Bortolami O, Stoppa G, Motola D, Vannacci A, et al.; DILI-IT Study Group. Antidepressant-induced acute liver injury: a case-control study in an Italian inpatient population. Drug Saf 2018; 41: 95-102. [PubMed: 28770534](Among 179 cases of hospitalizations for unexplained acute liver injury enrolled in a prospective study between 2010 and 2014, 17 had been exposed to antidepressants including two receiving tricyclic antidepressants, but none were reported as receiving doxepin).
- Review Amitriptyline.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Amitriptyline.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Desipramine.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Desipramine.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Imipramine.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Imipramine.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Protriptyline.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Protriptyline.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Antidepressant Agents.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Antidepressant Agents.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Doxepin - LiverToxDoxepin - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...