NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Dicyclomine is an anticholinergic agent used to treat gastrointestinal conditions such as acid peptic disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Dicyclomine has not been implicated in causing liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent acute liver injury.
Background
Dicyclomine (dye sye' kloe meen) is synthetic tertiary amine, antispasmotic and anticholinergic agent which inhibits the muscarinic actions of acetylcholine on autonomic nerve endings, decreasing gastrointestinal secretions and intestinal motility. Dicyclomine has broad activity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, but has been used largely for gastrointestinal conditions including peptic ulcer disease and gastrointestinal conditions associated with pain and spasm. Dicyclomine was approved for use in the United States for the treatment of peptic ulcer disease in 1996, but is now more commonly used as an antispasmotic to treat irritable bowel syndrome. Dicyclomine is available in capsules and tablets of 10 and 20 mg generically and under the brand name Bentyl. Oral syrups and solutions for injection are also available. The typical oral dose in adults is 10 to 20 mg four times daily. Common side effects are those of parasympathetic stimulation and include dryness of the mouth and eyes, decreased sweating, headache, visual blurring, constipation, urinary retention, anxiety, restlessness and delusions. Anticholinergic agents can precipitate acute narrow angle glaucoma and acute urinary retention.
Hepatotoxicity
Like other anticholinergic agents, dicyclomine has not been linked to episodes of liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver injury. The metabolism of dicyclomine is not well defined but it is likely metabolized by the liver.
References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of anticholinergics are given together in the Overview section on Anticholinergic Agents.
Drug Class: Anticholinergic Agents
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Dicyclomine – Generic, Bentyl®
DRUG CLASS
Anticholinergic Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dicyclomine | 77-19-0 | C19-H35-N-O2 |
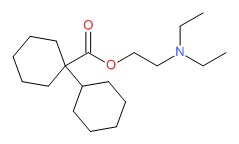 |
- Review Mepenzolate.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Mepenzolate.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Glycopyrrolate.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Glycopyrrolate.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Propantheline.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Propantheline.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome with Bentyl (dicyclomine hydrochloride).[J Clin Gastroenterol. 1981]Treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome with Bentyl (dicyclomine hydrochloride).Page JG, Dirnberger GM. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1981 Jun; 3(2):153-6.
- Review Fesoterodine.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Fesoterodine.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Dicyclomine - LiverToxDicyclomine - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...