NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Dapsone is a sulfonamide related drug used for the therapy of leprosy and dermatitis herpetiformis. Dapsone has been linked with rare cases of idiosyncratic liver injury, similar to that seen with the sulfonamides.
Background
Dapsone (dap' sone) is 4,4’ diaminodiphenylsulfone and is bacteriostatic for Mycobacterium leprae. Like other sulfonamides, dapsone is believed to act by inhibition of folate synthesis. Bacteria including M. leprae are acutely sensitive to this inhibition as folate is necessary for protein, DNA and RNA synthesis. In contast, humans are not affected by this inhibition of folate synthesis because they rely upon dietary sources of folate. Dapsone was approved for use in the United States in 1979. Current indications include leprosy and dermatitis herpetiformis. Off-label uses include prophylaxis against pneumocystis jiroveci (formerly carinii) in HIV infected patients. Dapsone is available in multiple generic forms in tablets of 25 and 100 mg. Dapsone is usually started at a low dose in the range of 50 mg daily and titrated upward to a total daily dose of 100 to 300 mg. In the therapy of leprosy, the combination of dapsone with clofazimine and rifampin is recommended for 6 or 12 months followed by monotherapy with dapsone until all signs of clinical activity are controlled and biopsies are negative for at least a year. Up-to-date and reliable information on the management of leprosy is available from the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Clinical Center, Baton Rouge, LA: https://www.hrsa.gov/hansens-disease/clinical-center.html. Dapsone is also available as a topical gel for therapy of acne. Common side effects of oral dapsone include hemolysis and anemia, nausea, abdominal pain, tinnitus, vertigo, blurred vision, headache, insomnia, and rash. Dapsone is not uncommonly associated more severe side effects including peripheral neuropathy, acute psychosis, nephrotic syndrome, acute liver injury, hemolysis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hypersensitivity reactions and a lupus-like syndrome.
Hepatotoxicity
Dapsone, like other sulfonamides, causes a characteristic idiosyncratic liver injury that has features of drug-allergy or hypersensitivity. The typical onset is sudden development of fever and rash followed by jaundice within a few days or weeks of starting the medication. Eosinophilia or lymphocytosis are also common. The presentation can resemble acute mononucleosis and is often referred to as "sulfone syndrome" which is a variant of the "drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms" (DRESS) syndrome. The pattern of injury is typically cholestatic or mixed and can be complicated and prolonged. In rare instances, dapsone induced liver injury has resulted in acute liver failure. However, most cases resolve rapidly, usually within 2 to 4 weeks of stopping dapsone, unless cholestasis is severe.
Likelihood score: A (well known cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Mechanism of Injury
The clinical pattern of injury with dapsone suggests a drug-allergy or hypersensitivity mechanism, perhaps through its metabolism to a toxic, reactive or antigenic metabolite.
Outcome and Management
Dapsone induced liver injury can result in acute liver failure, but most cases resolve rapidly with discontinuation of drug and full recovery is expected within 2 to 8 weeks. Severe cholestatic injury may be prolonged. Rechallenge should not be done, and patients should be told that they are allergic to sulfonamides (“sulfa-drugs”) and not receive other drugs in this class. If dapsone is considered crucial for management, attempts at desensitization can be made. Prednisone has been used to treat dapsone related liver injury with variable success, but may be particularly helpful in patients with prominent allergic features with systemic features and fever, rash, and eosinophilia.
References to the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of dapsone are given in the Overview on Sulfonamides.
Drug Class: Antiinfective Agents, Sulfonamides
Other Drugs in this Subclass, Leprosy Agents: Clofazimine, Rifampin
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Dapsone – Generic
DRUG CLASS
Antiinfective Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
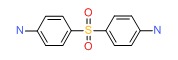
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NO | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dapsone | 80-08-0 | C12-H12-N2-O2-S |
 |
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- Review Sulfonamides.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Sulfonamides.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- [Agranulocytosis induced by dapsone prescribed for dermatitis herpetiformis].[Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1996][Agranulocytosis induced by dapsone prescribed for dermatitis herpetiformis].Machet L, Callens A, Mercier E, Gargot S, Lorette G, Vaillant L. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1996; 123(5):328-30.
- Review Update on the use of dapsone in dermatology.[Int J Dermatol. 2020]Review Update on the use of dapsone in dermatology.Ghaoui N, Hanna E, Abbas O, Kibbi AG, Kurban M. Int J Dermatol. 2020 Jul; 59(7):787-795. Epub 2020 Jan 7.
- A lethal case of the dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome involving the myocardium.[Neth J Med. 2016]A lethal case of the dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome involving the myocardium.Hoogeveen RM, van der Bom T, de Boer HH, Thurlings RM, Wind BS, de Vries HJ, van Lent AU, Beuers U, van der Wal AC, Nellen FJ. Neth J Med. 2016 Feb; 74(2):89-92.
- Early Onset Dapsone-induced Photosensitive Dermatitis: A Rare Side Effect of a Common Drug.[Indian J Lepr. 2015]Early Onset Dapsone-induced Photosensitive Dermatitis: A Rare Side Effect of a Common Drug.Karjigi S, Murthy SC, Kallappa H, Kusuma MR, Reddy YN. Indian J Lepr. 2015 Jul-Sep; 87(3):161-4.
- Dapsone - LiverToxDapsone - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...