NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Carvedilol is a unique antihypertensive medication with activity against both alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors. Carvedilol has been linked to at least one instance of clinically apparent liver injury.
Background
Carvedilol (kar' ve dil" ol) is a unique beta-blocker and antihypertensive agent that has both alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptor blocking activity. The beta-blockade is nonselective, acting on both beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors. Beta-1 adrenergic blockade reduces the heart rate and myocardial contractility by slowing the AV conduction and suppressing automaticity. Beta-2 blockade affects peripheral vascular resistance and can cause bronchospasm and hypoglycemia. The alpha-adrenergic blockade acts on alpha-1 receptors which results in relaxation of arterial smooth muscle and vasodilation. Carvedilol was approved for use in the United States in 1995 and is still in wide use with more than 2.5 million prescriptions filled yearly. Current indications include hypertension and heart failure. Carvedilol is also approved for use after myocardial infarction to reduce cardiovascular mortality. Carvedilol is also used off label to treat migraine and vascular headaches. Carvedilol is available in tablets of 3.125, 6.25, 12.5 and 25 mg in generic forms and under the trade name Coreg. The typical initial oral dose in adults is 6.25 mg twice daily, with subsequent dose modification based upon clinical response and tolerance, the average total daily maintenance dose being 25 to 50 mg. Extended release capsules of 10, 20, 40 and 80 mg capsules which can be given once daily are also available. Common side effects of carvedilol include bradycardia, hypotension, fatigue, dizziness, depression, memory loss, impotence, cold limbs and less commonly severe hypotension, heart failure and bronchospasm. Sudden withdrawal can trigger rebound hypertension. Beta-blockers are contraindicated in patients with asthma, bradycardia and heart failure and should be used cautiously in the elderly and in patients with diabetes.
Hepatotoxicity
Mild-to-moderate elevations in serum aminotransferase levels occur in less than 2% of patients on carvedilol and are usually transient and asymptomatic, resolving even with continuation of therapy. Despite its wide spread use, carvedilol has been linked to only a single case of clinically apparent liver injury, with injury arising 6 months after starting therapy and a mixed pattern of enzyme elevations without jaundice or signs of hypersensitivity or autoimmunity, and rapid recovery on stopping. Thus, clinically apparent liver injury from carvediol is exceeding rare.
Likelihood score: D (Possible rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Mechanism of Injury
Carvedilol undergoes extensive metabolism by the liver into both active and inactive metabolites and its excretion is largely biliary. The mechanism of liver injury due to carvedilol is unknown but is likely to be an idiosyncratic reaction to the drug or a metabolite.
References to the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of carvedilol are provided in the overview on Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, last updated in June 2019.
Drug Class: Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Carvedilol – Generic, Coreg®
DRUG CLASS
Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
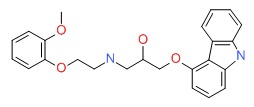
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carvedilol | 72956-09-3 | C24-H26-N2-O4 |
 |
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- [The effect of carvedilol on cardiac function and autoantibodies against the cardiac receptors].[Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za ...][The effect of carvedilol on cardiac function and autoantibodies against the cardiac receptors].Chen J, Hu DY, Zhang L, Liu XL, Wu YF, Li J. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2005 Jun; 33(6):498-501.
- Effects of carvedilol on adrenergic receptor pharmacology in human ventricular myocardium and lymphocytes.[Clin Investig. 1992]Effects of carvedilol on adrenergic receptor pharmacology in human ventricular myocardium and lymphocytes.Bristow MR, Larrabee P, Müller-Beckmann B, Minobe W, Roden R, Skerl L, Klein J, Handwerger D, Port JD. Clin Investig. 1992; 70 Suppl 1:S105-13.
- Review Carvedilol, a novel vasodilating beta-blocker with the potential for cardiovascular organ protection.[Eur Heart J. 1996]Review Carvedilol, a novel vasodilating beta-blocker with the potential for cardiovascular organ protection.Feuerstein GZ, Ruffolo RR Jr. Eur Heart J. 1996 Apr; 17 Suppl B:24-9.
- Studies on the mechanism of arterial vasodilation produced by the novel antihypertensive agent, carvedilol.[Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1991]Studies on the mechanism of arterial vasodilation produced by the novel antihypertensive agent, carvedilol.Nichols AJ, Gellai M, Ruffolo RR Jr. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1991; 5(1):25-38.
- Review The pharmacology of carvedilol.[Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1990]Review The pharmacology of carvedilol.Ruffolo RR Jr, Gellai M, Hieble JP, Willette RN, Nichols AJ. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1990; 38 Suppl 2:S82-8.
- Carvedilol - LiverToxCarvedilol - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...