NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Ubrogepant is a small molecule inhibitor of the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor that blocks the action of CGRP, a potent vasodilator believed to play a role in migraine headaches. Ubrogepant is approved for treatment of acute migraine attacks. In clinical trials, urbrogepant was generally well tolerated with only rare instances of transient serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy and with no reported instances of clinically apparent liver injury.
Background
Ubrogepant (ue broe’ je pant) is a small molecule inhibitor of the receptor for the calcitonin gene- related peptide (CGRP), which is believed to play a role in the pathogenesis of migraine headaches. CGRP is a potent vasodilator and pain-signaling neurotransmitter that is found throughout the central and peripheral nervous system but is particularly common in trigeminal ganglia. Levels of CGRP are elevated during episodes of migraine headache, and administration of the peptide can induce migraines in susceptible patients. For this reason, approaches to inhibition of CGRP signaling were developed as potential therapies for migraine, both as preventive therapies to decrease the rate of migraine as well as for treatment of acute attacks. Several monoclonal antibodies that block CGRP or its receptor are approved for use in prevention of migraines and two small molecule inhibitors of the CGRP receptor (the “gepants”: ubrogepant and rimegepant) are available for treatment of acute migraine. In several randomized, placebo controlled trials, ubrogepant in oral doses of 50 or 100 mg was found to increase the rate of being free from headache pain 2 hours after dosing (19% to 26% compared to 9% to 11% with placebo). Ubrogepant was approved for treatment of acute migraine in the United States in 2019 and is available in tablets of 50 and 100 mg under the brand name Ubrelvy. The recommended dose is 50 or 100 mg orally as soon as possible after onset of migraine with the option to repeat the dose after 2 hours but not to exceed 200 mg during any 24 hour period. Ubrogepant can be safely given in patients receiving preventive therapy with monoclonal antibodies to CGRP or its receptor. Ubrogepant is generally well tolerated with side effects of nausea, dizziness, somnolence and dry mouth that are generally uncommon (<5%), transient and mild-to-moderate in severity. Severe adverse events have not been reported.
Hepatotoxicity
In preregistration controlled trials of ubrogepant in several thousand patients, mild-to-moderate serum aminotransferase elevations arose in a small percentage of patients (1% to 2%) and overall rates were not different from those in placebo recipients. In the controlled trials and subsequently with general use, there have been no reports of clinically apparent liver injury attributed to ubrogepant. In contrast, telcagepant, the initial oral CGRP receptor antagonist evaluated as therapy for migraine headaches, was abandoned during development because of several instances of clinically apparent liver injury in recipients that was characterized by marked elevations in serum aminotransferase levels and symptoms of fatigue, nausea and abdominal discomfort arising within 2 to 4 weeks of starting therapy which rapidly resolved with prompt stopping of therapy. Similar episodes have not been reported with ubrogepant.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent acute liver injury).
Mechanism of Injury
Possible mechanisms of liver injury due to ubrogepant are not known. It is metabolized in the liver largely by CYP 3A4 and is susceptible to drug-drug interactions with agents that induced or inhibit this microsomal enzyme. Lower doses should be used in patients receiving CYP 3A4 inhibitors.
Outcome and Management
Drug Class: Migraine Headache Agents
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Ubrogepant – Ubrelvy®
DRUG CLASS
Migraine Headache Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
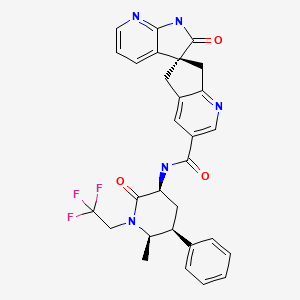
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NO. | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ubrogepant | 1374248-77-7 | C29-H26-F3-N5-O3 |
|
ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
References updated: 20 July 2021
Abbreviations: CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide.
- Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1999.(Review of hepatotoxicity published in 1999 before the availability of CGRP antagonists).
- FDA. https://www
.accessdata .fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs /nda/2019/211765Orig1s000MedR.pdf. (FDA Drug Approvals website that has product labels [package inserts], letters of approval and full FDA multidisciplinary scientific review of the ubrogepant application including specific discussion of hepatic adverse events which consisted mainly of mild-to-moderate ALT or AST elevations which were similar in frequency in ubrogepant vs placebo recipients and two patients with clinically apparent liver injury had evidence of a pre-existing and unrelated diagnosis; cholecystitis and pancreatitis). - Ho TW, Connor KM, Zhang Y, Pearlman E, Koppenhaver J, Fan X, Lines C, et al. Randomized controlled trial of the CGRP receptor antagonist telcagepant for migraine prevention. Neurology. 2014;83:958–66. [PubMed: 25107879](Among 660 patients with migraine enrolled in a controlled trial of telcagepant [140 or 280 mg] vs placebo twice daily for 12 weeks, 13 patients on telcagepant developed ALT elevations above 3 times ULN, generally between weeks 4 and 6 of treatment, and in two instances rising to 33 and 39 times ULN accompanied by symptoms but not jaundice leading to prompt discontinuation and to early termination of the trial because of the risk of significant hepatotoxicity).
- Voss T, Lipton RB, Dodick DW, Dupre N, Ge JY, Bachman R, Assaid C, et al. A phase IIb randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ubrogepant for the acute treatment of migraine. Cephalalgia. 2016;36:887–98. [PubMed: 27269043](Among 834 patients treated with ubrogepant [1, 10, 25, 50 or 100 mg] or placebo for an acute attack of migraine, 26% of those receiving 100 mg were headache pain free at 2 hours compared to 9% on placebo, while adverse events more frequent with ubrogepant included low rates of nausea and dizziness and there were no ALT elevations above 3 times ULN).
- Tfelt-Hansen P, Loder E. The Emperor's new gepants: are the effects of the new oral CGRP antagonists clinically meaningful? Headache. 2019;59:113–7. [PubMed: 30451300](Commentary on the relative efficacy of two oral CGRP receptor antagonists, ubrogepant and rimegepant, which show only modest efficacy in acute migraine [therapeutic gain of 5-8%] and only when compared to placebo as compared to well-known effective therapies such as aspirin and other nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents [8-14%] and the triptans [16-32%]).
- Goadsby PJ, Tepper SJ, Watkins PB, Ayele G, Miceli R, Butler M, Severt L, et al. Safety and tolerability of ubrogepant following intermittent, high-frequency dosing: Randomized, placebo-controlled trial in healthy adults. Cephalalgia. 2019;39:1753–61. [PMC free article: PMC6900570] [PubMed: 31537107](Study of safety of ubrogepant given in intermittent doses [200 mg per day for 2 days] to healthy adults found the overall adverse event rates were the same as with placebo [44% vs 45%], including headache [11% vs 10%] and ALT elevations of 3 times ULN or more [in 5 on placebo and 2 on ubrogepant], which were transient and resolved even with drug continuation and without bilirubin elevations or symptoms).
- Lipton RB, Dodick DW, Ailani J, Lu K, Finnegan M, Szegedi A, Trugman JM. Effect of ubrogepant vs placebo on pain and the most bothersome associated symptom in the acute treatment of migraine: the ACHIEVE II randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019;322:1887–98. [PMC free article: PMC6865323] [PubMed: 31742631](Among 1465 adults with an acute migraine headache, freedom from pain at 2 hours was achieved by 21% and 22% of ubrogepant [25 or 50 mg] vs 14% of placebo recipients, while adverse events of nausea and dizziness were generally mild and uncommon [~ 2%] and ALT or AST elevations of at least 3 times ULN arose in only 4 of 966 [<1%] rimegepant treated patients, all of which were transient and without symptoms or jaundice).
- Dodick DW, Lipton RB, Ailani J, Lu K, Finnegan M, Trugman JM, Szegedi A. Ubrogepant for the treatment of migraine. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2230–41. [PubMed: 31800988](Among 1672 adults with migraine headache, freedom from pain within 2 hours was achieved by 19% and 21% of ubrogepant recipients [50 or 100 mg] vs 12% of placebo recipients, and adverse events of dry mouth, somnolence and nausea were generally mild and uncommon [less than 5%], while ALT or AST elevations of 3 times ULN or greater arose in 0.4% and 0.6% vs 0.2% of patients on placebo).
- Ailani J, Lipton RB, Hutchinson S, Knievel K, Lu K, Butler M, Yu SY, et al. Long-term safety evaluation of ubrogepant for the acute treatment of migraine: phase 3,randomized, 52-week extension trial. Headache. 2020;60:141–52. [PMC free article: PMC7004213] [PubMed: 31913519](Among 1230 adults randomized to ubrogepant [50 or 100 mg] or usual care to treat migraine attacks over a 52 week period, elevations in ALT arose in 31% and 32% on ubrogepant vs 31% on usual care and were above 3 times ULN in 1.3% and 2.7% vs 1%, but none of the elevations were associated with jaundice or symptoms).
- Ankrom W, Bondiskey P, Li CC, Palcza J, Liu W, Dockendorf MF, Matthews C, et al. Ubrogepant is not associated with clinically meaningful elevations of alanine aminotransferase in healthy adult males. Clin Transl Sci. 2020;13:462–72. [PMC free article: PMC7214647] [PubMed: 31899602](In two pharmacokinetic and safety studies conducted in 72 healthy male adults, ubrogepant in single and multiple doses of 40 to 400 mg daily for up to 28 days was well tolerated with no serious adverse events or ALT elevations above 3 times ULN; overall rates of ALT abnormalities were similar to those with placebo).
- Scott LJ. Ubrogepant: first approval. Drugs. 2020;80:323–8. [PMC free article: PMC7062659] [PubMed: 32020557](Review of the mechanism of action, history of development, pharmacology, clinical efficacy and safety of ubrogepant shortly after its approval for use in the US, mentions that ALT or AST elevations above 3 times ULN arose in 1-3% of patients, but none were associated with jaundice and rates were similar between ubrogepant and placebo recipients).
- Lasmiditan (Reyvow) and ubrogepant (Ubrelvy) for acute treatment of migraine. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2020;62(1593):35–9. [PubMed: 32555120](Concise review of the mechanism of action, clinical efficacy, safety and costs of ubrogepant and lasmiditan as therapy of acute migraine shortly after their approval for this indication in the US, mentions side effects of ubrogepant being nausea and somnolence but does not mention ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Rimegepant (Nurtec ODT) for acute treatment of migraine. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2020;62(1597):70–2. [PubMed: 32555113](Concise review of the mechanism of action, pharmacology, clinical efficacy, safety and cost of rimegepant shortly after its approval in the US as therapy of acute migraine in adults, mentions that it “was generally well tolerated in clinical trials; nausea was the most common adverse event [~2%]”).
- Drugs for migraine. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2020;62(1608):153–60. [PubMed: 33434187](Concise summary of the relative clinical efficacy, safety and costs of drugs to treat acute migraine headache [such as analgesics, opiates, triptans, ergots and oral CGRP receptor antagonists] and to prevent migraines [such as anticonvulsants, beta blockers, antidepressants and the monoclonal antibodies to CGRP and its receptor]).
- Hutchinson S, Dodick DW, Treppendahl C, Bennett NL, Yu SY, Guo H, Trugman JM. Ubrogepant for the acute treatment of migraine: pooled efficacy, safety, and tolerability from the ACHIEVE I and ACHIEVE II phase 3 randomized trials. Neurol Ther. 2021;10:235–49. [PMC free article: PMC8140011] [PubMed: 33608814](Post hoc analysis of efficacy and safety from two controlled trials in 2240 patients with migraine, found pain-free rates at 2 hours to be 20.5% with ubrogepant vs 13% with placebo with similar overall rates of adverse events [11.5% vs 11.2%] and no serious adverse events requiring discontinuation).
- Jakate A, Blumenfeld AM, Boinpally R, Butler M, Borbridge L, Contreras-De Lama J, McGeeney D, et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of ubrogepant when coadministered with calcitonin gene-related peptide-targeted monoclonal antibody migraine preventives in participants with migraine: A randomized phase 1b drug-drug interaction study. Headache. 2021;61:642–52. [PMC free article: PMC8252052] [PubMed: 33818780](Among 40 patients enrolled in pharmacokinetic studies of ubrogepant with or without concurrent preventive therapy with erenumab or galcanezumab, pharmacokinetic parameters were similar with and without concurrent monoclonal antibodies to CGRP and adverse event rates appeared to be unaffected; there were “no clinically relevant changes in laboratory parameters”).
- Robbins MS. Diagnosis and management of headache: a review. JAMA. 2021;325:1874–85. [PubMed: 33974014](Review of the diagnosis and management of headache including use of calcitonin gene-related peptide antagonists for acute migraine attacks which has uncommon side effects of dry mouth and dizziness; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Rimegepant.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Rimegepant.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Ubrogepant to treat migraine.[Drugs Today (Barc). 2020]Ubrogepant to treat migraine.Dhir A. Drugs Today (Barc). 2020 Jul; 56(7):459-467.
- Ubrogepant Is Not Associated With Clinically Meaningful Elevations of Alanine Aminotransferase in Healthy Adult Males.[Clin Transl Sci. 2020]Ubrogepant Is Not Associated With Clinically Meaningful Elevations of Alanine Aminotransferase in Healthy Adult Males.Ankrom W, Bondiskey P, Li CC, Palcza J, Liu W, Dockendorf MF, Matthews C, Panebianco D, Reynders T, Wagner JA, et al. Clin Transl Sci. 2020 May; 13(3):462-472. Epub 2020 Jan 3.
- Long-Term Safety Evaluation of Ubrogepant for the Acute Treatment of Migraine: Phase 3, Randomized, 52-Week Extension Trial.[Headache. 2020]Long-Term Safety Evaluation of Ubrogepant for the Acute Treatment of Migraine: Phase 3, Randomized, 52-Week Extension Trial.Ailani J, Lipton RB, Hutchinson S, Knievel K, Lu K, Butler M, Yu SY, Finnegan M, Severt L, Trugman JM. Headache. 2020 Jan; 60(1):141-152.
- Review Ubrogepant for the treatment of migraine.[Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020]Review Ubrogepant for the treatment of migraine.Curto M, Capi M, Cipolla F, Cisale GY, Martelletti P, Lionetto L. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 May; 21(7):755-759. Epub 2020 Feb 3.
- Ubrogepant - LiverToxUbrogepant - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...