NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Revefenacin is a synthetic anticholinergic agent that is used as a once daily, nebulized inhalant for maintenance treatment of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Revefenacin has not been implicated in causing liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent acute liver injury.
Background
Revefenacin (rev" e fen' a sin) is a synthetic anticholinergic which inhibits the muscarinic actions of acetylcholine on autonomic nerve endings, which decreases bronchial smooth muscle contractions and can alleviate bronchospasm in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Revefenacin has potent activity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptors found in bronchial smooth muscle (M3). Its quaternary ammonium structure decreases its ability to cross lipid membranes such as the blood brain barrier. Revefenacin was approved for use in the United States in 2018 for use as a once daily respiratory inhalant for maintenance treatment of bronchospasm associated with COPD. Revefenacin is available under the brand name Yupelri as an inhalation solution in multiuse vials of 175 mcg in 3 mL. The recommended dose in adults is 175 mcg by inhalation once daily. When given by inhaler, revefenacin has minimal systemic absorption and few anticholinergic side effects. Side effects are mild but can include the headache, cough, symptoms of upper respiratory infections and back pain. Revefenacin is not recommended for patients with hepatic impairment, and concurrent use of other anticholinergic agents should be avoided. Potential severe adverse events include paradoxical bronchospasm, narrow-angle glaucoma, urinary retention and immediate hypersensitivity reactions.
Hepatotoxicity
Like other anticholinergic agents, revefenacin has not been linked to episodes of liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver injury. Another reason for its hepatic safety may relate to its low systemic absorption when administered by inhaler.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Drug Class: Anticholinergic Agents
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Revefenacin – Yupelri®
DRUG CLASS
Anticholinergic Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
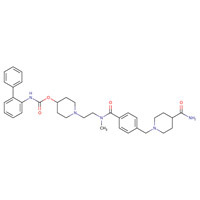
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revefenacin | 864750-70-9 | C35-H43-N5-O4 |
 |
ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
References updated: 12 April 2019
Abbreviations: COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Barnes PJ. Pulmonary pharmacology. In, Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2018, pp. 727-49.(Textbook of pharmacology and therapeutics).
- Pudi KK, Barnes CN, Moran EJ, Haumann B, Kerwin E. A 28-day, randomized,double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study of nebulized revefenacin in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res 2017; 18: 182. [PMC free article: PMC5667509] [PubMed: 29096627](Among 355 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD] treated with nebulized revefenacin [44, 88, 175, or 350 mcg] or placebo once daily for 28 days, forced expiratory volume improved more with the higher doses than with placebo, and adverse event rates were similar in all groups, systemic anticholinergic effects being uncommon).
- Quinn D, Barnes CN, Yates W, Bourdet DL, Moran EJ, Potgieter P, Nicholls A, et al. Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics and safety of revefenacin (TD-4208), a long-acting muscarinic antagonist, in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Results of two randomized, double-blind, phase 2 studies. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2018; 48: 71-9. [PubMed: 28987804](Among 59 patients with COPD treated with once daily nebulized revefenacin or placebo for 7 days, forced expiratory volume improved with all doses of revefenacin compared to placebo, and adverse events were mild and similar in rates in all groups).
- Heo YA. Revefenacin: first global approval. Drugs 2019; 79: 85-91. [PMC free article: PMC6445810] [PubMed: 30560478](Review of the development, clinical efficacy and safety of revefenacin, an inhaled, long acting muscarinic antagonist approved for use in patients with COPD; mentions that the frequency and severity of adverse events were “generally similar across treatment groups”; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Revefenacin (Yupelri) for COPD. Med Lett Drugs Ther 2019; 61: 14-5. [PubMed: 30856160](Concise review of the maintenance therapy of COPD and the clinical efficacy, safety and costs of revefenacin shortly after its approval in the US as a once daily nebulized inhalant for the management treatment of patients with COPD; does not mention ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- https://www
.accessdata .fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/ (FDA Drug Approvals website that has product labels [package inserts], letters of approval and full FDA scientific review of the new drug application for safety and efficacy; mentions that there were no differences in laboratory test results between revefenacin and comparator arms of pre-licensure clinical trials and the one patient who developed clinically apparent liver injury during revefenacin treatment was found to have pancreatic cancer as a cause of jaundice).
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Cardiovascular safety of revefenacin, a once-daily, lung-selective, long-acting muscarinic antagonist for nebulized therapy of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Evaluation in phase 3 clinical trials.[Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2019]Cardiovascular safety of revefenacin, a once-daily, lung-selective, long-acting muscarinic antagonist for nebulized therapy of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Evaluation in phase 3 clinical trials.Donohue JF, Feldman G, Sethi S, Barnes CN, Pendyala S, Bourdet D, Crater G. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Aug; 57:101808. Epub 2019 May 30.
- A 28-day, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study of nebulized revefenacin in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[Respir Res. 2017]A 28-day, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study of nebulized revefenacin in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Pudi KK, Barnes CN, Moran EJ, Haumann B, Kerwin E. Respir Res. 2017 Nov 2; 18(1):182. Epub 2017 Nov 2.
- Revefenacin, a once-daily, lung-selective, long-acting muscarinic antagonist for nebulized therapy: Safety and tolerability results of a 52-week phase 3 trial in moderate to very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[Respir Med. 2019]Revefenacin, a once-daily, lung-selective, long-acting muscarinic antagonist for nebulized therapy: Safety and tolerability results of a 52-week phase 3 trial in moderate to very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Donohue JF, Kerwin E, Sethi S, Haumann B, Pendyala S, Dean L, Barnes CN, Moran EJ, Crater G. Respir Med. 2019 Jul; 153:38-43. Epub 2019 May 23.
- Review Revefenacin, a once-daily, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, for nebulized maintenance therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2021]Review Revefenacin, a once-daily, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, for nebulized maintenance therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Hvisdas C. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2021 Jun 23; 78(13):1184-1194.
- Review Revefenacin for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020]Review Revefenacin for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Clark CM, Jacobs DM, Sethi S. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020 Mar; 14(3):239-247. Epub 2019 Dec 25.
- Revefenacin - LiverToxRevefenacin - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...