NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Esmolol is a cardioselective beta-blocker used in parenteral forms in the treatment of arrhythmias and severe hypertension. Esmolol has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent drug induced liver injury.
Background
Esmolol (es' moe lol) is considered a “selective” beta-adrenergic receptor blocker in that it has potent activity against beta-1 adrenergic receptors which are found in cardiac muscle, but has little or no activity against beta-2 adrenergic receptors found on bronchial and vascular smooth muscle. Esmolol has a rapid time of onset and short duration of action, which makes it useful for intravenous therapy of acute arrhythmias and severe hypertension or in patients with hypertension who are unable to take oral medications. Esmolol was approved for use in the United States in 1986 and is currently used for the intravenous therapy of supraventricular tachycardias, hypertension in the perioperative period and during episodes of acute myocardial ischemia or infarction. Esmolol is available in liquid formulations in vials and ampules for injection generically and under the trade name of Brevibloc. The usual intravenous dose of esmolol is 50 to 200 mcg/kg/minute, sometimes after a loading dose of 500 mcg/kg/minute. Common side effects include bradycardia, hypotension, fatigue, dizziness, depression, agitation, and confusion. At high doses, esmolol is less cardioselective and can induce acute bronchospasm. As with all beta-blockers, sudden withdrawal can trigger rebound hypertension.
Hepatotoxicity
Esmolol therapy has not been clearly associated with serum aminotransferase elevations or with clinically apparent, acute liver injury. It is often used in critically patients and generally for a short period only. Thus, hepatotoxicity due to esmolol must be very rare, if it occurs at all. Most commonly used beta-blockers have been linked to rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury, typically with onset within 2 to 12 weeks, a hepatocellular pattern of liver enzyme elevations, rapid recovery upon withdrawal, and little evidence of hypersensitivity (rash, fever, eosinophilia) or autoantibody formation. Similar instances have not been reported after esmolol use.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Mechanism of Injury
The mechanism of drug induced liver injury from beta-blockers such as esmolol is not known. Esmolol undergoes rapid hydrolysis by plasma esterases and is rapidly excreted by the kidneys as inactive metabolites. The rare case of liver injury from beta-blockers is likely to be due to an idiosyncratic reaction.
Outcome and Management
The severity of liver injury due to beta-blockers ranges from mild serum aminotransferase elevations to acute hepatitis with jaundice. In large case series of drug induced liver injury and acute liver failure due to medications, esmolol has not been listed as a potential cause. There is little information about cross reactivity among the beta-blockers to hepatic injury. Switching from a beta-blocker that has caused acute liver injury to another should be done with caution and active monitoring.
References to the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of esmolol are provided in the overview on Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, last updated in June 2019.
Drug Class: Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Esmolol – Generic, Brevibloc®
DRUG CLASS
Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
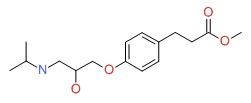
| Esmolol | 103598-03-4 | C16-H25-N-O4 |
 |
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- Esmolol: a novel cardioselective, titratable, intravenous beta-blocker with ultrashort half-life.[Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1987]Esmolol: a novel cardioselective, titratable, intravenous beta-blocker with ultrashort half-life.Covinsky JO. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1987 Apr; 21(4):316-21.
- Review Esmolol: a titratable short-acting intravenous beta blocker for acute critical care settings.[Am Heart J. 1987]Review Esmolol: a titratable short-acting intravenous beta blocker for acute critical care settings.Turlapaty P, Laddu A, Murthy VS, Singh B, Lee R. Am Heart J. 1987 Oct; 114(4 Pt 1):866-85.
- Review Clinical pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy of esmolol.[Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012]Review Clinical pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy of esmolol.Wiest DB, Haney JS. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012 Jun 1; 51(6):347-56.
- Bolus doses of esmolol for the prevention of perioperative hypertension and tachycardia.[Can J Anaesth. 1990]Bolus doses of esmolol for the prevention of perioperative hypertension and tachycardia.Oxorn D, Knox JW, Hill J. Can J Anaesth. 1990 Mar; 37(2):206-9.
- Review Esmolol: a review of its use in the short-term treatment of tachyarrhythmias and the short-term control of tachycardia and hypertension.[Drugs. 2012]Review Esmolol: a review of its use in the short-term treatment of tachyarrhythmias and the short-term control of tachycardia and hypertension.Garnock-Jones KP. Drugs. 2012 Jan 1; 72(1):109-32.
- Esmolol - LiverToxEsmolol - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...