NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Cevimeline is an orally available cholinergic agonist that is used to treat symptoms of dry mouth in patients with keratoconjunctivitis sicca (Sjögren syndrome). Cevimeline has not been linked to serum enzyme elevations during therapy or to instances of clinically apparent liver injury.
Background
Cevimeline (se vim' e leen) is a quinuclidine derivative of acetylcholine which acts as a cholinergic muscarinic agonist. Engagement of the muscarinic cholinergic receptors causes increased secretion from exocrine glands, including sweat, salivary, lacrimal, gastric, pancreatic and intestinal glands, as well as increase smooth muscle tone and motility in the eye, respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract. Use of daily doses of cevimeline has been shown to improve symptoms of dry mouth and increase salivary flow in patients with Sjögren syndrome and with xerostomia due to local irradiation therapy. Cevimeline was approved for use in the United States in 2000 and is available in capsules of 30 mg generically and under the brand name Evoxac. The typical dose is 30 mg three times daily. Side effects are usually mild and largely attributable to cholinergic stimulation including increased sweating, rhinitis, nausea, diarrhea, headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances and fatigue.
Hepatotoxicity
In prelicensure trials of cevimeline, serum enzyme elevations were no more frequent than with placebo and there were no reports of acute liver injury. Since licensure and more wide scale use, cevimeline has remained free of association with instances of clinically apparent liver injury.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Mechanism of Injury
The mechanism by which cevimeline might cause serum aminotransferase elevations is not known. Cevimeline is metabolized by the liver predominantly by the cytochrome P450 system, CYP 2D6 and 3A4, but neither inhibits nor induces the microsomal enzymes.
Drug Class: Sjögren Syndrome Agents, Cholinergic Agents
Other Drugs in the Class: Pilocarpine
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Cevimeline – Evoxac®
DRUG CLASS
Sjögren Syndrome Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
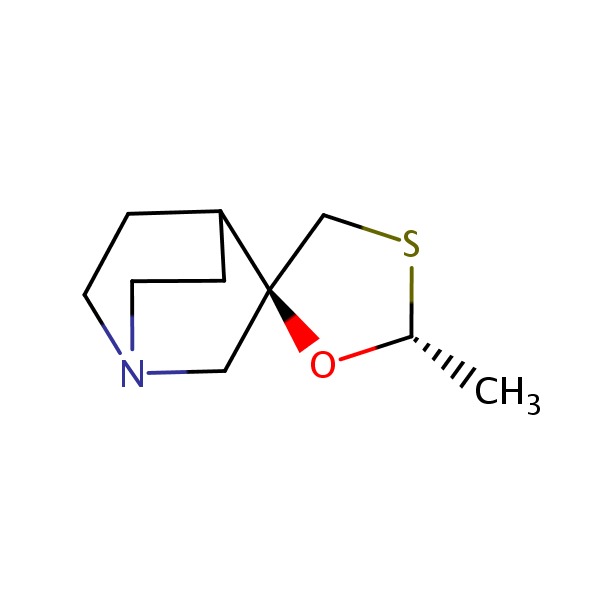
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NO. | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cevimeline | 107233-08-9 | C10-H17-N-O-S |
 |
ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
References updated: 23 January 2017
- Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1999.(Extensive review of hepatotoxicity published in 1999; cholinergic agents and cevimeline are not discussed).
- Kaplowitz N, DeLeve LD, eds. Drug-induced liver disease. 3rd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013.(Textbook of hepatotoxicity published in 2013; cholinergic agents and cevimeline are not discussed).
- Brown JH, Laiken N. Muscarinic receptor agonists and antagonists. In, Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman.s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 12th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2011, pp. 219-37.(Textbook of pharmacology and therapeutics).
- Cevimeline(Evoxac) for dry mouth. Med Lett Drugs Ther 2000; 42(1084): 70. [PubMed: 10932302](Concise review of mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, efficacy, safety and cost of cevimeline, mentions side effects of sweating, nausea, rhinitis, diarrhea and visual disturbances; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Fife RS, Chase WF, Dore RK, Wiesenhutter CW, Lockhart PB, Tindall E, Suen JY. Cevimeline for the treatment of xerostomia in patients with Sjögren syndrome: a randomized trial. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162: 1293-300. [PubMed: 12038948](Controlled trial of 2 doses [30 and 60 mg three times daily] for 6 weeks in 75 patients with Sjögren syndrome showed dose related decrease in symptoms of dry mouth and increase in salivary flow; side effects were largely those of cholinergic stimulation and "there were no apparent dose-related changes in mean laboratory values").
- Petrone D, Condemi JJ, Fife R, Gluck O, Cohen S, Dalgin P. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of cevimeline in Sjögren's syndrome patients with xerostomia and keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46: 748-54. [PubMed: 11920411](Controlled trial of 2 doses of cevimeline [15 and 30 mg three times daily] versus placebo in 197 patients with Sjögren syndrome showed dose related improvements in dry mouth and salivary flow and "there were no significant dose-related changes in mean laboratory values").
- Fox RI. Sjögren's syndrome: evolving therapies. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2003; 12: 247-54. [PubMed: 12556218](Review of standard and experimental therapies of Sjögren syndrome mentions cevimeline, but does not discuss its adverse side effects).
- Ono M, Takamura E, Shinozaki K, Tsumura T, Hamano T, Yagi Y, Tsubota K. Therapeutic effect of cevimeline on dry eye in patients with Sjögren's syndrome: a randomized, double-blind clinical study. Am J Ophthalmol 2004; 138: 6-17. [PubMed: 15234277](Among 60 patients with Sjögren syndrome who were treated cevimeline [20 or 30 mg three times daily] or placebo for 4 weeks, the most frequent side effects were diarrhea, nausea, dyspepsia, and headache; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Chambers MS, Jones CU, Biel MA, Weber RS, Hodge KM, Chen Y, Holland JM, et al. Open-label, long-term safety study of cevimeline in the treatment of postirradiation xerostomia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007; 69: 1369-76. [PubMed: 17855005](Among 255 patients with post-irradiation xerostomia who were treated with cevimeline [45 mg three times daily] for 6 months, common side effects were sweating [48%], dyspepsia [9%], nausea [8%] and diarrhea [6%]; mild elevations in ALT occurred, but were less than twice ULN).
- Chalasani N, Bonkovsky HL, Fontana R, Lee W, Stolz A, Talwalkar J, Reddy KR, et al.; United States Drug Induced Liver Injury Network. Features and outcomes of 899 patients with drug-induced liver injury: the DILIN prospective study. Gastroenterology 2015; 148: 1340-1352. [PMC free article: PMC4446235] [PubMed: 25754159](Among 899 cases of drug induced liver injury enrolled in a US prospective study between 2004 and 2013, no cases were attributed to cevimeline).
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Pilocarpine.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Pilocarpine.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of cevimeline in Sjögren's syndrome patients with xerostomia and keratoconjunctivitis sicca.[Arthritis Rheum. 2002]A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of cevimeline in Sjögren's syndrome patients with xerostomia and keratoconjunctivitis sicca.Petrone D, Condemi JJ, Fife R, Gluck O, Cohen S, Dalgin P. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar; 46(3):748-54.
- Cevimeline for the treatment of xerostomia in patients with Sjögren syndrome: a randomized trial.[Arch Intern Med. 2002]Cevimeline for the treatment of xerostomia in patients with Sjögren syndrome: a randomized trial.Fife RS, Chase WF, Dore RK, Wiesenhutter CW, Lockhart PB, Tindall E, Suen JY. Arch Intern Med. 2002 Jun 10; 162(11):1293-300.
- Cevimeline.[Drugs. 2008]Cevimeline.Weber J, Keating GM. Drugs. 2008; 68(12):1691-8.
- Review Treatment of primary Sjögren syndrome: a systematic review.[JAMA. 2010]Review Treatment of primary Sjögren syndrome: a systematic review.Ramos-Casals M, Tzioufas AG, Stone JH, Sisó A, Bosch X. JAMA. 2010 Jul 28; 304(4):452-60.
- Cevimeline - LiverToxCevimeline - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...