NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Buspirone is a psychoactive drug used for management of general anxiety disorders and alleviation of the symptoms of anxiety. Despite wide scale use, it is an infrequent cause of serum enzyme elevations and has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice.
Background
Buspirone (bue spye' rone) is an azapirone antianxiety medication that has little or no similarity to the benzodiazepines or barbiturates in its structure or mechanism of action. Buspirone appears to interact with dopamine and serotonin receptors, but its precise mechanism of action in alleviating anxiety is not known. Buspirone was approved for use in the United States in 1986. Current indications are for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder and amelioration of the symptoms of anxiety. It has been used off label for depression (often in combination with other agents) and as treatment for substance abuse, posttraumatic stress syndrome, bruxism, tardive dyskinesia and other psychiatric and neurological conditions, but its efficacy in these situations has not been proven. Buspirone is available in tablets of 5, 10, 15 and 30 mg in several generic forms and under the brand name Buspar. Typical doses are 15 to 30 mg daily in divided doses. Side effects may include drowsiness, headache, nausea, abdominal discomfort and rash.
Hepatotoxicity
Buspirone has been associated with infrequent serum aminotransferase elevations, but has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent liver injury in the published literature. Indeed, buspirone is often used as a control, noncytotoxic agent in assessment of other psychotropic drugs in vitro and in vivo. Buspirone is, nevertheless, metabolized in the liver by the P450 system (CYP 3A4) and has the potential of causing drug-drug interactions.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Drug Class: Sedatives and Hypnotics, Miscellaneous
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Buspirone – Generic, Buspar®
DRUG CLASS
Sedatives and Hypnotics
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
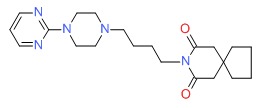
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buspirone | 36505-84-7 | C21-H31-N5-O2 |
 |
ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
References updated: 11 September 2017
- Zimmerman HJ. Unconventional drugs. Miscellaneous drugs and diagnostic chemicals. In, Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1999, pp. 731-4.(Expert review of hepatotoxicity published in 1999; buspirone is not discussed).
- Larrey D, Ripault M-P. Anxiolytic agents. Hepatotoxicity of psychotropic drugs and drugs of abuse. In, Kaplowitz N, DeLeve LD, eds. Drug-induced liver disease. 3rd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013, pp. 455-6.(Review of hepatotoxicity of hypnotics and sedatives discusses benzodiazepines, buspirone and valerian all of which have been linked to rare cases of liver injury).
- Mihic SJ, Harris RA. Hypnotics and sedatives. In, Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 12th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2011, pp. 457-80.(Textbook of pharmacology and therapeutics).
- Jacobson AF, Dominguez RA, Goldstein BJ, Steinbook RM. Comparison of buspirone and diazepam in generalized anxiety disorder. Pharmacotherapy 1985; 5: 290-6. [PubMed: 2866493](Controlled trial of buspirone vs diazepam in 66 patients with anxiety disorders found similar efficacy and fewer side effects with buspirone and "no significant differences in either groups in final laboratory assessments").
- Newton RE, Marunycz JD, Alderdice MT, Napoliello MJ. Review of the side-effect profile of buspirone. Am J Med 1986; 80 (3B): 17-21. [PubMed: 2870641](Analysis of side effects among 984 patients with general anxiety disorders treated with buspirone in controlled trials; side effects occurring more often with buspirone than placebo included dizziness [9% vs 2%], headache [7% vs 2%], nervousness, diarrhea, paresthesias, excitation and sweating; laboratory test results were not discussed).
- Robinson D, Napoliello MJ, Schenk J. The safety and usefulness of buspirone as an anxiolytic drug in elderly versus young patients. Clin Ther 1988; 10: 740-6. [PubMed: 3219687](Open label postmarketing study of buspirone in 6000 patients; side effects were reported in 6-7% of patients, but no laboratory results were reported).
- Feighner JP, Cohn JB. Analysis of individual symptoms in generalized anxiety--a pooled, multistudy, double-blind evaluation of buspirone. Neuropsychobiology1989; 21 (3): 124-30. [PubMed: 2615929](Pooled data on 427 patients with anxiety disorders treated with buspirone [10 to 60 mg daily] for 4 weeks; "the beneficial effects of buspirone were not compromised by any significant side effects").
- Rakel RE. Long-term buspirone therapy for chronic anxiety: a multicenter international study to determine safety. South Med J 1990; 83: 194-8. [PubMed: 2406933](Among 424 patients with chronic anxiety treated with buspirone for at least 6 months, side effects were mild to moderate in severity and "clinical laboratory tests, including hematologic and hepatic indices, revealed no clinically significant changes attributable to buspirone").
- Sheehan DV, Raj AB, Harnett-Sheehan K, Soto S, Knapp E. The relative efficacy of high-dose buspirone and alprazolam in the treatment of panic disorder: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1993; 88: 1-11. [PubMed: 8372689](Controlled trial of buspirone vs alprazolam vs placebo in 92 patients with panic disorders identified no changes in laboratory test results in buspirone treated subjects).
- Sramek JJ, Frackiewicz EJ, Cutler NR. Efficacy and safety of two dosing regimens of buspirone in the treatment of outpatients with persistent anxiety. Clin Ther 1997; 19: 498-506. [PubMed: 9220214](Controlled trial of 2 doses of buspirone in 137 patients with anxiety disorders; common side effects were dizziness, headache, nausea, diarrhea and somnolence; there were no differences in laboratory test results in the treated patients).
- Sramek JJ, Hong WW, Hamid S, Nape B, Cutler NR. Meta-analysis of the safety and tolerability of two dose regimens of buspirone in patients with persistent anxiety. Depress Anxiety 1999; 9: 131-4. [PubMed: 10356651](Pooled analysis of safety in studies of two doses of buspirone found no differences in laboratory tests and no mention of clinically apparent liver injury).
- McRae-Clark AL, Carter RE, Killeen TK, Carpenter MJ, Wahlquist AE, Simpson SA, Brady KT. A placebo-controlled trial of buspirone for the treatment of marijuana dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend 2009; 105: 132-8. [PMC free article: PMC2789590] [PubMed: 19699593](Controlled trial of 12 weeks of buspirone vs placebo in 50 patients with marijuana dependence found no serious adverse events, but no laboratory test results reported).
- Chalasani N, Fontana RJ, Bonkovsky HL, Watkins PB, Davern T, Serrano J, Yang H, Rochon J; Drug Induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN). Causes, clinical features, and outcomes from a prospective study of drug-induced liver injury in the United States. Gastroenterology 2008; 135: 1924-34. (Among 300. [PMC free article: PMC3654244] [PubMed: 18955056]cases of drug induced liver disease in the US collected from 2004 to 2008, 14 were attributed to antidepressants, including 6 to duloxetine, 3 atomoxetine, 2 fluoxetine, 2 bupropion, and 1 sertraline, but none to buspirone).
- Ravindran LN, Stein MB. The pharmacologic treatment of anxiety disorders: a review of progress. J Clin Psychiatry 2010; 71: 839-54. [PubMed: 20667290](Review of the use of medications for anxiety disorders including tricyclic antidepressants, MAO inhibitors, SSRIs, benzodiazepines and buspirone states that buspirone has good tolerability and low potential for dependence but is of limited efficacy).
- Reinhold JA, Mandos LA, Rickels K, Lohoff FW. Pharmacological treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2011; 12: 2457-67. [PubMed: 21950420](Review of pharmacological therapy of anxiety disorders, the first line agents being the SSRIs and SNRIs; buspirone has comparable but slightly weaker efficacy compared to benzodiazepines; no mention of adverse events).
- Loane C, Politis M. Buspirone: what is it all about? Brain Res 2012; 1461: 111-8. [PubMed: 22608068](Review of efficacy and safety of buspirone and its use in other conditions such as depression, ataxia, dyskinesia and obsessive compulsive disorder; no discussion of adverse events).
- Hernández N, Bessone F, Sánchez A, di Pace M, Brahm J, Zapata R, A Chirino R, et al. Profile of idiosyncratic drug induced liver injury in Latin America: an analysis of published reports. Ann Hepatol 2014; 13: 231-9. [PubMed: 24552865](Among 176 reports of drug induced liver injury from Latin America published between 1996 and 2012, none were attributed to buspirone).
- Chalasani N, Bonkovsky HL, Fontana R, Lee W, Stolz A, Talwalkar J, Reddy KR, et al.; United States Drug Induced Liver Injury Network. Features and outcomes of 899 patients with drug-induced liver injury: The DILIN Prospective Study. Gastroenterology 2015; 148: 1340-52.e7. [PMC free article: PMC4446235] [PubMed: 25754159](Among 899 cases of drug induced liver injury enrolled in a US prospective study between 2004 and 2013, none were attributed to buspirone or other sedative or antianxiety medications).
- Review Marijuana.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Marijuana.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Analysis of individual symptoms in generalized anxiety--a pooled, multistudy, double-blind evaluation of buspirone.[Neuropsychobiology. 1989]Analysis of individual symptoms in generalized anxiety--a pooled, multistudy, double-blind evaluation of buspirone.Feighner JP, Cohn JB. Neuropsychobiology. 1989; 21(3):124-30.
- The safety and usefulness of buspirone as an anxiolytic drug in elderly versus young patients.[Clin Ther. 1988]The safety and usefulness of buspirone as an anxiolytic drug in elderly versus young patients.Robinson D, Napoliello MJ, Schenk J. Clin Ther. 1988; 10(6):740-6.
- A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of buspirone for the treatment of anxiety in opioid-dependent individuals.[Am J Addict. 2004]A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of buspirone for the treatment of anxiety in opioid-dependent individuals.McRae AL, Sonne SC, Brady KT, Durkalski V, Palesch Y. Am J Addict. 2004 Jan-Feb; 13(1):53-63.
- Review Ozanimod.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Ozanimod.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Buspirone - LiverToxBuspirone - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...