Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
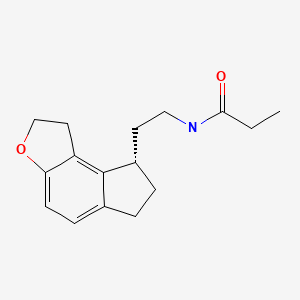
CASRN: 196597-26-9
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Data from one patient indicates that ramelteon and its principle active metabolite have low levels in milk. Monitor the infant for drowsiness and adequate feeding, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Until more data become available an alternate drug may be preferred.
Drug Levels
Ramelteon undergoes rapid and almost complete first-pass metabolism to several metabolites. The principle active metabolite is M-II, which has an elimination half-life of 2 to 5 hours in adults.
Maternal Levels. A woman was taking oral ramelteon 8 mg nightly for sleep during pregnancy and postpartum while nursing. Breastmilk concentrations of ramelteon and its active M-II metabolite were measured at 3 times postpartum: on day 1 at 8.2 hours after a dose, concentrations were 0.4 and 14.6 mcg/L, respectively; day 2 at 9.1 hours after the dose, concentrations were 0.2 and 7.1 mcg/L, respectively; day 3 at 2.2 hours after the dose, concentrations were 2.6 and 88.9 mcg/L, respectively. The authors calculated that the infant would receive 0.24% of the mother’s weight-adjusted dosage.[1]
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Prolactin levels increased by 4.9 mcg/L (34%) in non-breastfeeding women with chronic insomnia who were taking ramelteon 16 mg nightly for 6 months. No clinical symptoms of hyperprolactinemia were reported.[2] The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed.
References
- 1.
- Saito J, Tachibana Y, Sano Wada Y, et al. Presence of hypnotics in the cord blood and breast milk, with no adverse effects in the infant: A case report. Breastfeed Med. 2022;17:349–52. [PubMed: 34935466]
- 2.
- Richardson G, Wang-Weigand S. Effects of long-term exposure to ramelteon, a melatonin receptor agonist, on endocrine function in adults with chronic insomnia. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2009;24:103–11. [PubMed: 19090503]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Ramelteon
CAS Registry Number
196597-26-9
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Kinetic resolution of an indan derivative using Bacillus sp. SUI-12: synthesis of a key intermediate of the melatonin receptor agonist TAK-375.[J Biosci Bioeng. 2002]Kinetic resolution of an indan derivative using Bacillus sp. SUI-12: synthesis of a key intermediate of the melatonin receptor agonist TAK-375.Tarui N, Nagano Y, Sakane T, Matsumoto K, Kawada M, Uchikawa O, Ohkawa S, Nakahama K. J Biosci Bioeng. 2002; 93(1):44-7.
- Review Lovastatin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Lovastatin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Effect of ramelteon (TAK-375), a selective MT1/MT2 receptor agonist, on motor performance in mice.[Neurosci Lett. 2006]Effect of ramelteon (TAK-375), a selective MT1/MT2 receptor agonist, on motor performance in mice.Miyamoto M. Neurosci Lett. 2006 Jul 24; 402(3):201-4. Epub 2006 May 24.
- Effects of ramelteon (TAK-375) on nocturnal sleep in freely moving monkeys.[Brain Res. 2004]Effects of ramelteon (TAK-375) on nocturnal sleep in freely moving monkeys.Yukuhiro N, Kimura H, Nishikawa H, Ohkawa S, Yoshikubo S, Miyamoto M. Brain Res. 2004 Nov 19; 1027(1-2):59-66.
- Review Simvastatin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Simvastatin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Ramelteon - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Ramelteon - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
