NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). Genes and Disease [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 1998-.
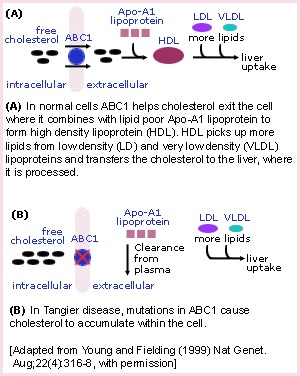
Tangier disease (TD) is a genetic disorder of cholesterol transport named for the secluded island of Tangier, located off the coast of Virginia. TD was first identified in a five-year-old inhabitant of the island who had characteristic orange tonsils, very low levels of high density lipoprotein (HDL) or 'good cholesterol', and an enlarged liver and spleen.
TD is caused by mutations in the ABC1 (ATP-binding cassette) gene on chromosome 9q31. ABC1 codes for a protein that helps rid cells of excess cholesterol. This cholesterol is then picked up by HDL particles in the blood and carried to the liver, which processes the cholesterol to be reused in cells throughout the body. Individuals with TD are unable to eliminate cholesterol from cells, leading to its buildup in the tonsils and other organs.
The discovery of this important cholesterol transport gene may lead to a better understanding of the inverse relationship between HDL levels and coronary artery disease, an important killer in the US. New drugs that regulate HDL levels may be developed and such drugs would not only help individuals with TD, but also people with more common disorders such as familial HDL deficiency. This is a good illustration of how research into rare diseases can sometimes help more common disorders.
- Genome view see gene locations
- Entrez Gene collection of gene-related information
- BLink related sequences in different organisms
- Research articles online full text
- Books online books section
- OMIM catalog of human genes and disorders
- American Heart Association fighting heart disease and stroke
- National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, NIH cardiovascular information
- Tangier disease - Genes and DiseaseTangier disease - Genes and Disease
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
