OVERVIEW
Introduction
Hyoscyamine as a natural plant alkaloid derivative and anticholinergic that is used to treat mild to moderate nausea, motion sickness, hyperactive bladder and allergic rhinitis. Hyoscyamine has not been implicated in causing liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent acute liver injury.
Background
Hyoscyamine (hye" oh sye' a meen) is a derivative of natural alkaloid found in plants of the Solanacea family such as henbane (Hyoscyamus niger, for which it is named), jimson weed (Datura stramonium), tomatoes (Soanum lycopersicum) and deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna). Hyoscyamine is the levorotary isomer of atropine and has potent anticholinergic, antimuscarinic activity. It has been used for decades as an antiemetic, antisecretory and antispasmotic agent in the treatment of nausea, motion sickness, allergic rhinitis, gastrointestinal spasm and hypermotility, functional bowel syndrome and hyperactive bladder. Despite having been used in clinical medicine for decades, hyoscyamine has not been formally approved for many of its common uses in the United States. Hyoscyamine is available as tablets, capsules, liquids, elixirs, powders, and solutions for injection in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. Common brand names for products that include hyoscyamine are Belladonna Alkaloids, Donnatal, Hyomax, Urogesic, and Cyclospaz. The recommended adult oral dose varies, but is generally 0.125 to 0.25 mg two to four times daily. Common side effects are those of parasympathetic stimulation and include dryness of the mouth and eyes, decreased sweating, headache, visual blurring, constipation, urinary retention, impotence, tachycardia and palpitations, anxiety, restlessness and in some instances agitation and hallucinations. Anticholinergic agents can precipitate acute narrow angle glaucoma and acute urinary retention.
Hepatotoxicity
Despite widespread use over many decades, hyoscyamine has not been linked to episodes of liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver injury. A major reason for its safety may relate to the low daily dose and limited duration of use.
References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of anticholinergics are given together after the Overview section on Anticholinergic Agents.
Drug Class: Gastrointestinal Agents; Anticholinergic Agents
PRODUCT INFORMATION
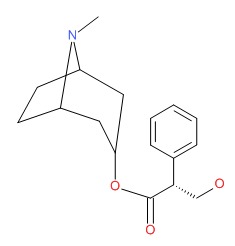
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
Publication Details
Publication History
Last Update: July 7, 2017.
Copyright
Publisher
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda (MD)
NLM Citation
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-. Hyoscyamine. [Updated 2017 Jul 7].