CASRN: 59-42-7
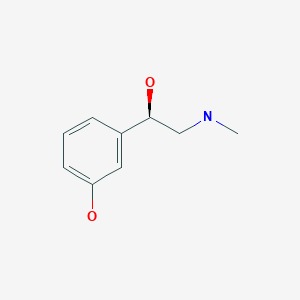
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
The oral bioavailability of phenylephrine is only about 40%,[1] so the drug is unlikely to reach the infant in large amounts. However, intravenous or oral administration of phenylephrine might decrease milk production. Because no information is available on the use of oral phenylephrine during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant.
Phenylephrine nasal spray or ophthalmic drops are less likely to decrease lactation. To substantially diminish the effect of the drug after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information in humans was not found as of the revision date. However, animal data indicate that phenylephrine can decrease milk production[2][3] and pseudoephedrine, a pharmacologically similar vasoconstrictor, decreases milk production in nursing mothers after oral use.[4]
Alternate Drugs to Consider
References
- 1.
- Eccles R. Substitution of phenylephrine for pseudoephedrine as a nasal decongeststant. An illogical way to control methamphetamine abuse. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;63:10-4. [PMC free article: PMC2000711] [PubMed: 17116124]
- 2.
- Bruckmaier R, Mayer H, Schams D. Effects of alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists in intramammary pressure and milk flow in dairy cows. J Dairy Res. 1991;58:411-9. [PubMed: 1684977]
- 3.
- Inderwies T, Pfaffl MW, Bruckmaier RM. Milking characteristics and their relation to adrenergic receptor mRNA expression and ligand binding in the mammary gland of dairy cows. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2003;25:275-86. [PubMed: 14550511]
- 4.
- Aljazaf K, Hale TW, Ilett KF et al. Pseudoephedrine: effects on milk production in women and estimation of infant exposure via breastmilk. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;56:18-24. [PMC free article: PMC1884328] [PubMed: 12848771]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Phenylephrine
CAS Registry Number
59-42-7
Drug Class
- Breast Feeding
- Lactation
- Adrenergic Agents
- Adrenergic Alpha-Agonists
- Antiglaucoma Agents
- Sympathomimetics
- Vasoconstrictor Agents
- Nasal Decongestants
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
Publication Details
Publication History
Last Revision: October 31, 2018.
Copyright
Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Publisher
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Bethesda (MD)
NLM Citation
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-. Phenylephrine. [Updated 2018 Oct 31].