From: The BLAST Sequence Analysis Tool

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
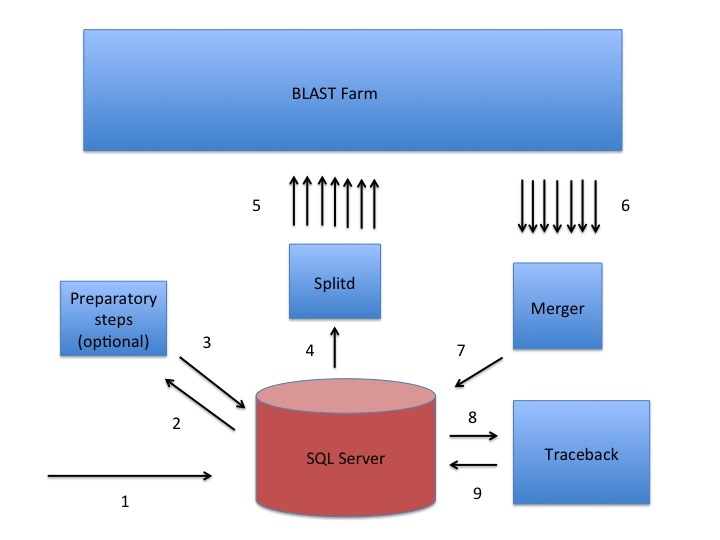
A sketch of the Splitd system used at the NCBI for processing BLAST requests. The numbers in the figure identify steps in the process. First, the search is inserted into the SQL database as ASN.1 [1]. Second, an optional preparatory step may retrieve data from Entrez or produce a PSSM using RPSBLAST [2, 3]. Third, Splitd pulls the search from the SQL database [4], queues it, and spreads it across several backends [5]. The search is processed on the BLAST farm. Results from backends are preliminary, because they include only the extent of alignments as well as the scores, but no insertions or deletions. Next, these results are sent to the Merger [6]. The Merger merges all pieces into one result which it stores in the SQL server [7]. The traceback then pulls the preliminary results from the SQL database and produces results that include insertions and deletions [8]. Finally, the traceback places the full results into the SQL database [9]. At this point the user may retrieve the results using the Request ID that the system issued.
From: The BLAST Sequence Analysis Tool

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.