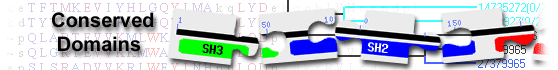E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM37 isoform d [Homo sapiens]
BBC and MATH_TRIM37 domain-containing protein( domain architecture ID 10649624)
BBC and MATH_TRIM37 domain-containing protein
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| MATH_TRIM37 | cd03773 | Tripartite motif containing protein 37 (TRIM37) family, MATH domain; TRIM37 is a peroxisomal ... |
151-284 | 9.06e-85 | |||
Tripartite motif containing protein 37 (TRIM37) family, MATH domain; TRIM37 is a peroxisomal protein and is a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) protein subfamily, also known as the RING-B-box-coiled-coil (RBCC) subfamily of zinc-finger proteins. Mutations in the human TRIM37 gene (also known as MUL) cause Mulibrey (muscle-liver-brain-eye) nanism, a rare growth disorder of prenatal onset characterized by dysmorphic features, pericardial constriction and hepatomegaly. TRIM37, similar to other TRIMs, contains a cysteine-rich, zinc-binding RING-finger domain followed by another cysteine-rich zinc-binding domain, the B-box, and a coiled-coil domain. TRIM37 is autoubiquitinated in a RING domain-dependent manner, indicating that it functions as an ubiquitin E3 ligase. In addition to the tripartite motif, TRIM37 also contains a MATH domain C-terminal to the coiled-coil domain. The MATH domain of TRIM37 has been shown to interact with the TRAF domain of six known TRAFs in vitro, however, it is unclear whether this is physiologically relevant. Eleven TRIM37 mutations have been associated with Mulibrey nanism so far. One mutation, Gly322Val, is located in the MATH domain and is the only mutation that does not affect the length of the protein. It results in the incorrect subcellular localization of TRIM37. : Pssm-ID: 239742 Cd Length: 132 Bit Score: 265.43 E-value: 9.06e-85
|
|||||||
| BBC | smart00502 | B-Box C-terminal domain; Coiled coil region C-terminal to (some) B-Box domains |
10-132 | 4.31e-28 | |||
B-Box C-terminal domain; Coiled coil region C-terminal to (some) B-Box domains : Pssm-ID: 128778 Cd Length: 127 Bit Score: 109.66 E-value: 4.31e-28
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| MATH_TRIM37 | cd03773 | Tripartite motif containing protein 37 (TRIM37) family, MATH domain; TRIM37 is a peroxisomal ... |
151-284 | 9.06e-85 | |||
Tripartite motif containing protein 37 (TRIM37) family, MATH domain; TRIM37 is a peroxisomal protein and is a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) protein subfamily, also known as the RING-B-box-coiled-coil (RBCC) subfamily of zinc-finger proteins. Mutations in the human TRIM37 gene (also known as MUL) cause Mulibrey (muscle-liver-brain-eye) nanism, a rare growth disorder of prenatal onset characterized by dysmorphic features, pericardial constriction and hepatomegaly. TRIM37, similar to other TRIMs, contains a cysteine-rich, zinc-binding RING-finger domain followed by another cysteine-rich zinc-binding domain, the B-box, and a coiled-coil domain. TRIM37 is autoubiquitinated in a RING domain-dependent manner, indicating that it functions as an ubiquitin E3 ligase. In addition to the tripartite motif, TRIM37 also contains a MATH domain C-terminal to the coiled-coil domain. The MATH domain of TRIM37 has been shown to interact with the TRAF domain of six known TRAFs in vitro, however, it is unclear whether this is physiologically relevant. Eleven TRIM37 mutations have been associated with Mulibrey nanism so far. One mutation, Gly322Val, is located in the MATH domain and is the only mutation that does not affect the length of the protein. It results in the incorrect subcellular localization of TRIM37. Pssm-ID: 239742 Cd Length: 132 Bit Score: 265.43 E-value: 9.06e-85
|
|||||||
| BBC | smart00502 | B-Box C-terminal domain; Coiled coil region C-terminal to (some) B-Box domains |
10-132 | 4.31e-28 | |||
B-Box C-terminal domain; Coiled coil region C-terminal to (some) B-Box domains Pssm-ID: 128778 Cd Length: 127 Bit Score: 109.66 E-value: 4.31e-28
|
|||||||
| MATH | smart00061 | meprin and TRAF homology; |
162-257 | 4.63e-11 | |||
meprin and TRAF homology; Pssm-ID: 214496 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 95 Bit Score: 60.01 E-value: 4.63e-11
|
|||||||
| MATH | pfam00917 | MATH domain; This motif has been called the Meprin And TRAF-Homology (MATH) domain. This ... |
163-276 | 5.90e-07 | |||
MATH domain; This motif has been called the Meprin And TRAF-Homology (MATH) domain. This domain is hugely expanded in the nematode C. elegans. Pssm-ID: 425944 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 113 Bit Score: 48.79 E-value: 5.90e-07
|
|||||||
| BAR_GRAF | cd07636 | The Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) domain of GTPase Regulator Associated with Focal adhesion kinase; ... |
36-138 | 2.89e-03 | |||
The Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) domain of GTPase Regulator Associated with Focal adhesion kinase; BAR domains are dimerization, lipid binding and curvature sensing modules found in many different proteins with diverse functions. GTPase Regulator Associated with Focal adhesion kinase (GRAF), also called Rho GTPase activating protein 26 (ARHGAP26), is a GAP with activity towards RhoA and Cdc42 and is only weakly active towards Rac1. It influences Rho-mediated cytoskeletal rearrangements and binds focal adhesion kinase (FAK), which is a critical component of integrin signaling. GRAF contains an N-terminal BAR domain, followed by a Pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, a Rho GAP domain, and a C-terminal SH3 domain. BAR domains form dimers that bind to membranes, induce membrane bending and curvature, and may also be involved in protein-protein interactions. The BAR domain of GRAF directly interacts with its Rho GAP domain and inhibits its activity. Autoinhibited GRAF is capable of binding membranes and tubulating liposomes, showing that the membrane-tubulation and GAP-inhibitory functions of the BAR domain can occur simultaneously. Pssm-ID: 153320 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 207 Bit Score: 40.04 E-value: 2.89e-03
|
|||||||
| COG5077 | COG5077 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase [Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, ... |
154-282 | 7.01e-03 | |||
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase [Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones]; Pssm-ID: 227409 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 1089 Bit Score: 40.24 E-value: 7.01e-03
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| MATH_TRIM37 | cd03773 | Tripartite motif containing protein 37 (TRIM37) family, MATH domain; TRIM37 is a peroxisomal ... |
151-284 | 9.06e-85 | |||
Tripartite motif containing protein 37 (TRIM37) family, MATH domain; TRIM37 is a peroxisomal protein and is a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) protein subfamily, also known as the RING-B-box-coiled-coil (RBCC) subfamily of zinc-finger proteins. Mutations in the human TRIM37 gene (also known as MUL) cause Mulibrey (muscle-liver-brain-eye) nanism, a rare growth disorder of prenatal onset characterized by dysmorphic features, pericardial constriction and hepatomegaly. TRIM37, similar to other TRIMs, contains a cysteine-rich, zinc-binding RING-finger domain followed by another cysteine-rich zinc-binding domain, the B-box, and a coiled-coil domain. TRIM37 is autoubiquitinated in a RING domain-dependent manner, indicating that it functions as an ubiquitin E3 ligase. In addition to the tripartite motif, TRIM37 also contains a MATH domain C-terminal to the coiled-coil domain. The MATH domain of TRIM37 has been shown to interact with the TRAF domain of six known TRAFs in vitro, however, it is unclear whether this is physiologically relevant. Eleven TRIM37 mutations have been associated with Mulibrey nanism so far. One mutation, Gly322Val, is located in the MATH domain and is the only mutation that does not affect the length of the protein. It results in the incorrect subcellular localization of TRIM37. Pssm-ID: 239742 Cd Length: 132 Bit Score: 265.43 E-value: 9.06e-85
|
|||||||
| BBC | smart00502 | B-Box C-terminal domain; Coiled coil region C-terminal to (some) B-Box domains |
10-132 | 4.31e-28 | |||
B-Box C-terminal domain; Coiled coil region C-terminal to (some) B-Box domains Pssm-ID: 128778 Cd Length: 127 Bit Score: 109.66 E-value: 4.31e-28
|
|||||||
| MATH | cd00121 | MATH (meprin and TRAF-C homology) domain; an independent folding unit with an eight-stranded ... |
158-282 | 1.64e-26 | |||
MATH (meprin and TRAF-C homology) domain; an independent folding unit with an eight-stranded beta-sandwich structure found in meprins, TRAFs and other proteins. Meprins comprise a class of extracellular metalloproteases which are anchored to the membrane and are capable of cleaving growth factors, extracellular matrix proteins, and biologically active peptides. TRAF molecules serve as adapter proteins that link cell surface receptors of the Tumor Necrosis Factor and 1nterleukin-1/Toll-like families to downstream kinase cascades, which results in the activation of transcription factors and the regulation of cell survival, proliferation and stress responses in the immune and inflammatory systems. Other members include the ubiquitin ligases, TRIM37 and SPOP, and the ubiquitin-specific proteases, HAUSP and Ubp21p. A large number of uncharacterized members mostly from lineage-specific expansions in C. elegans and rice contain MATH and BTB domains, similar to SPOP. The MATH domain has been shown to bind peptide/protein substrates in TRAFs and HAUSP. It is possible that the MATH domain in other members of this superfamily also interacts with various protein substrates. The TRAF domain may also be involved in the trimerization of TRAFs. Based on homology, it is postulated that the MATH domain in meprins may be involved in its tetramer assembly and that the MATH domain, in general, may take part in diverse modular arrangements defined by adjacent multimerization domains. Pssm-ID: 238068 Cd Length: 126 Bit Score: 105.15 E-value: 1.64e-26
|
|||||||
| MATH | smart00061 | meprin and TRAF homology; |
162-257 | 4.63e-11 | |||
meprin and TRAF homology; Pssm-ID: 214496 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 95 Bit Score: 60.01 E-value: 4.63e-11
|
|||||||
| MATH | pfam00917 | MATH domain; This motif has been called the Meprin And TRAF-Homology (MATH) domain. This ... |
163-276 | 5.90e-07 | |||
MATH domain; This motif has been called the Meprin And TRAF-Homology (MATH) domain. This domain is hugely expanded in the nematode C. elegans. Pssm-ID: 425944 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 113 Bit Score: 48.79 E-value: 5.90e-07
|
|||||||
| MATH_TRAF_C | cd00270 | Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor (TNFR)-Associated Factor (TRAF) family, TRAF domain, C-terminal ... |
161-281 | 7.38e-07 | |||
Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor (TNFR)-Associated Factor (TRAF) family, TRAF domain, C-terminal MATH subdomain; TRAF molecules serve as adapter proteins that link cell surface TNFRs and receptors of the interleukin-1/Toll-like family to downstream kinase signaling cascades which results in the activation of transcription factors and the regulation of cell survival, proliferation and stress responses in the immune and inflammatory systems. There are at least six mammalian and three Drosophila proteins containing TRAF domains. The mammalian TRAFs display varying expression profiles, indicating independent and cell type-specific regulation. They display distinct, as well as overlapping functions and interactions with receptors. Most TRAFs, except TRAF1, share N-terminal homology and contain a RING domain, multiple zinc finger domains, and a TRAF domain. TRAFs form homo- and heterotrimers through its TRAF domain. The TRAF domain can be divided into a more divergent N-terminal alpha helical region (TRAF-N), and a highly conserved C-terminal MATH subdomain (TRAF-C) with an eight-stranded beta-sandwich structure. TRAF-N mediates trimerization while TRAF-C interacts with receptors. Pssm-ID: 238168 Cd Length: 149 Bit Score: 49.53 E-value: 7.38e-07
|
|||||||
| MATH_Ubp21p | cd03775 | Ubiquitin-specific protease 21 (Ubp21p) family, MATH domain; composed of fungal proteins with ... |
155-282 | 2.81e-06 | |||
Ubiquitin-specific protease 21 (Ubp21p) family, MATH domain; composed of fungal proteins with similarity to Ubp21p of fission yeast. Ubp21p is a deubiquitinating enzyme that may be involved in the regulation of the protein kinase Prp4p, which controls the formation of active spliceosomes. Members of this family are similar to human HAUSP (Herpesvirus-associated ubiquitin-specific protease) in that they contain an N-terminal MATH domain and a C-terminal catalytic protease (C19 family) domain. HAUSP is also an ubiquitin-specific protease that specifically catalyzes the deubiquitylation of p53 and MDM2. The MATH domain of HAUSP contains the binding site for p53 and MDM2. Similarly, the MATH domain of members in this family may be involved in substrate binding. Pssm-ID: 239744 Cd Length: 134 Bit Score: 47.35 E-value: 2.81e-06
|
|||||||
| MATH_HAUSP | cd03772 | Herpesvirus-associated ubiquitin-specific protease (HAUSP, also known as USP7) family, ... |
159-281 | 1.15e-03 | |||
Herpesvirus-associated ubiquitin-specific protease (HAUSP, also known as USP7) family, N-terminal MATH (TRAF-like) domain; composed of proteins similar to human HAUSP, an enzyme that specifically catalyzes the deubiquitylation of p53 and MDM2, hence playing an important role in the p53-MDM2 pathway. It contains an N-terminal TRAF-like domain and a C-terminal catalytic protease (C19 family) domain. The tumor suppressor p53 protein is a transcription factor that responds to many cellular stress signals and is regulated primarily through ubiquitylation and subsequent degradation. MDM2 is a RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase that promotes p53 ubiquitinylation. p53 and MDM2 bind to the same site in the N-terminal TRAF-like domain of HAUSP in a mutually exclusive manner. HAUSP also interacts with the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) protein of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which efficiently immortalizes infected cells predisposing the host to a variety of cancers. EBNA1 plays several important roles in EBV latent infection and cellular transformation. It binds the same pocket as p53 in the HAUSP TRAF-like domain. Through interactions with p53, MDM2 and EBNA1, HAUSP plays a role in cell proliferation, apoptosis and EBV-mediated immortalization. Pssm-ID: 239741 Cd Length: 137 Bit Score: 39.74 E-value: 1.15e-03
|
|||||||
| BAR_GRAF | cd07636 | The Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) domain of GTPase Regulator Associated with Focal adhesion kinase; ... |
36-138 | 2.89e-03 | |||
The Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) domain of GTPase Regulator Associated with Focal adhesion kinase; BAR domains are dimerization, lipid binding and curvature sensing modules found in many different proteins with diverse functions. GTPase Regulator Associated with Focal adhesion kinase (GRAF), also called Rho GTPase activating protein 26 (ARHGAP26), is a GAP with activity towards RhoA and Cdc42 and is only weakly active towards Rac1. It influences Rho-mediated cytoskeletal rearrangements and binds focal adhesion kinase (FAK), which is a critical component of integrin signaling. GRAF contains an N-terminal BAR domain, followed by a Pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, a Rho GAP domain, and a C-terminal SH3 domain. BAR domains form dimers that bind to membranes, induce membrane bending and curvature, and may also be involved in protein-protein interactions. The BAR domain of GRAF directly interacts with its Rho GAP domain and inhibits its activity. Autoinhibited GRAF is capable of binding membranes and tubulating liposomes, showing that the membrane-tubulation and GAP-inhibitory functions of the BAR domain can occur simultaneously. Pssm-ID: 153320 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 207 Bit Score: 40.04 E-value: 2.89e-03
|
|||||||
| MATH_SPOP | cd03774 | Speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) family, MATH domain; composed of proteins with similarity to ... |
161-265 | 4.86e-03 | |||
Speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) family, MATH domain; composed of proteins with similarity to human SPOP. SPOP was isolated as a novel antigen recognized by serum from a scleroderma patient, whose overexpression in COS cells results in a discrete speckled pattern in the nuclei. It contains an N-terminal MATH domain and a C-terminal BTB (also called POZ) domain. Together with Cul3, SPOP constitutes an ubiquitin E3 ligase which is able to ubiquitinate the PcG protein BMI1, the variant histone macroH2A1 and the death domain-associated protein Daxx. Therefore, SPOP may be involved in the regulation of these proteins and may play a role in transcriptional regulation, apoptosis and X-chromosome inactivation. Cul3 binds to the BTB domain of SPOP whereas Daxx and the macroH2A1 nonhistone region have been shown to bind to the MATH domain. Both MATH and BTB domains are necessary for the nuclear speckled accumulation of SPOP. There are many proteins, mostly uncharacterized, containing both MATH and BTB domains from C. elegans and plants which are excluded from this family. Pssm-ID: 239743 Cd Length: 139 Bit Score: 38.30 E-value: 4.86e-03
|
|||||||
| COG5077 | COG5077 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase [Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, ... |
154-282 | 7.01e-03 | |||
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase [Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones]; Pssm-ID: 227409 [Multi-domain] Cd Length: 1089 Bit Score: 40.24 E-value: 7.01e-03
|
|||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|